Farrowing induction, why?
Before implementing a farrowing induction policy on your farm, first ask if there is a reason to do so? Do farm records indicate too many stillbirths (eg.≥ 10%)? Is neonatal mortality too high? If the answer to either question is yes, then improved supervision of piglet births with assistance as needed, will improve piglet survival. Problems during farrowing leading to long piglet birth intervals (eg. >45 min) may result in a lack of oxygen (anoxia), which can kill piglets or may be non-lethal but result in poorer viability that pre-disposes to piglet neonatal mortality.
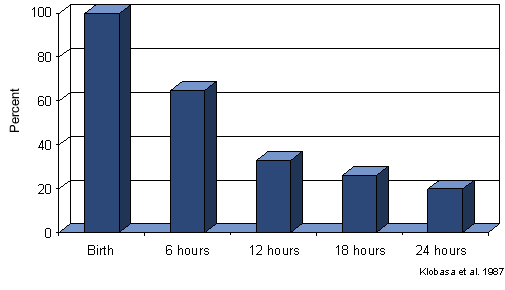
Other important reasons to supervise farrowing include colostrum management and effective cross-fostering. Pigs born weak, or that become chilled, or pigs born into a very large litter may not get enough colostrum and so their passive immunity is reduced. These pigs will be more easily infected with disease organisms that they can then carry into the nursery to infect others as their passive immunity declines. Control programs for PRRS and PMWS are examples of situations where ensuring adequate colostrum uptake is emphasized. Regarding cross-fostering, the best place for any baby is with it’s own mother so avoid fostering just to even out litters, if sows have enough functional teats for their litter leave the pigs where they are. If pigs are to be fostered, realize that by 6 hours, immunoglobulin content of colostrum has declined >30% and by 12 hours, by 60% (Figure 1). The ability of pigs to absorb immunoglobulins also declines at a similar rate. Clearly, the donor and recipient sows need to be chosen carefully.
Farrowing induction timing
The timing of farrowing induction is important. The average gestation length may be as low as 113 days or as high as 117 days so, determine the average gestation length on each individual farm and then do not induce more than 2-days before due date. The pig foetus is unusual in that its saccular phase of lung development is exponential; at 100 days of gestation there are no alveoli and by about 114 days of gestation, lungs are fully developed. Therefore, a relatively small error in timing of parturition can result in a major deficiency of lung development. The fat content of the colostrum from induced sows may be lower but immunoglobulin content will not be affected.
Injecting prostaglandin F2α (PGF) or its analogues is effective for induction of farrowing, although a large range in the interval between treatment and farrowing is usual. Experience has shown that only 50% to 60% of PGF-treated sows farrow during the working day after injection and only these sows are candidates for farrowing supervision. If sows receive PGF but are not supervised during farrowing, then the cost of the PGF is borne by those sows that are supervised, effectively increasing the cost of treatment per sow. However, the cost of farrowing induction can be reduced because we now know that if injected into the vulva, PGF at 50% (or even 25%) of the manufacturers recommended dose is equally as effective as an IM injection at the full dose (Table 1). If this route of injection is chosen, use a 12 mm, 20 g needle, or one even smaller. The injection site is external where the vulva meets the skin of the rump and sows tolerate this very well (Figure 2). Vulva mucosal injection is also used, but mucosal injection stings and has been associated with haematomas, and so is not recommended on welfare grounds.
Table 1. Effect of dose and site of prostaglandin injection on time of farrowing
| Full dose, IM | 50% dose, IM | 50% dose, vulva | 25% dose, vulva | |
| Farrow 8-24 h, % | 19 |
12 |
18 |
15 |
| Farrow 24-32 h, % |
50 |
41 |
61 |
62 |
| Farrow >32 h, % |
31 |
47 |
21 |
23 |
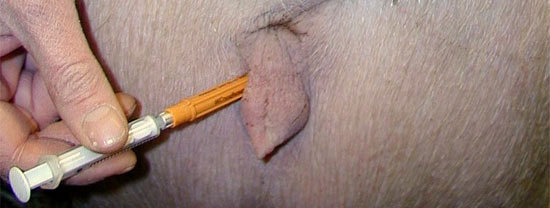
Figure 2. The needle shown is obviously too big for this route of injection. It merely shows where to inject.
The injection of oxytocin 20-24 hours after the injection of PGF, and before any piglet is delivered, has been shown to causes a more rapid onset of farrowing, but may also cause an interrupted farrowing, ie. a piglet is delivered but then farrowing stops, necessitating manual assistance and excessive intervention is a risk factor for urogenital disease. Oxytocin is a potent hormone and, regardless of label indications, there is little or no reason to inject more than 10 IU oxytocin for any reason. When 30 or 40 IU oxytocin was given after farrowing has started (ie. first pig delivered), an increase in dystocia still occurred and higher numbers of stillbirths were observed. Further, the stillbirths were occurring among the first few pigs rather than the expected last few pigs of the litter (Table 2). The was because the oxytocin caused severe uterine contractions, which traumatized umbilical chords and caused foetal anoxia, as evidenced by more piglets being born with meconium staining. Taken together, it is suggested that oxytocin not be used at farrowing except therapeutically in cases of slow farrowing.
Table 2. Effect of oxytocin after delivery of the first pig on farrowing performance
| Control | 30 IU | 40 IU | |
| Dystocia, % | 5 |
10 |
20 |
| Liveborn |
8.3 |
8.7 |
8.7 |
| Stillborn (SB) |
0.3 |
0.6 |
0.6 |
| SB pigs 1-4, % | 0 |
70.8 |
40.0 |
| SB pigs 5-8, % | 16.6 |
8.3 |
20.0 |
| SB pigs ≥ 9 | 83.3 |
20.8 |
40.0 |
A further method shown to improve the predictability of farrowing is a double injection of PGF (‘split dose’). With this technique, an injection of PGF is given in the morning and then a second PGF injection is given 6 to 8 hours later. When this is done, a higher proportion of sows will farrow the next day during working hours (Table 3), so facilitating farrowing supervision.
Table 3. Effect of split-dose prostaglandin injections on timing of farrowing
| Hours from PGF to start of farrowing | ||||
| 0-8 |
8-22 |
22-32 |
>32 | |
| Single dose |
8 |
17 |
56 |
19 |
| Split dose |
4 |
10 | 84 | 2 |
Conclusions
In conclusion, if levels of stillbirths or neonatal mortality are a concern then, if done correctly, farrowing induction will improve the ability to supervise piglet deliveries and potentially save an average of 0.5 pigs per litter. I recommend the split dose injection (50% each time) but further recommend that oxytocin be reserved for slow deliveries and after delivery of the 5th or 6th pig to ensure a prompt completion of farrowing.





