After the banning of antibiotics as growth promoters, there was an increase in their total consumption due to the therapeutics treatments.
Total use of antibiotics in Denmark

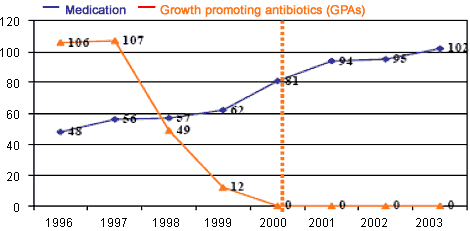
Changes in the use of antibiotics in Denmark
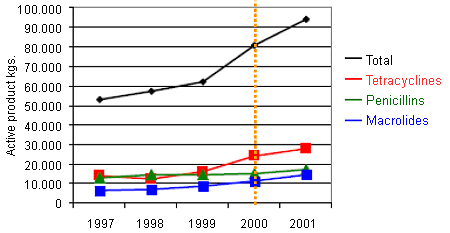
Waddel J. DVM. Sutton veterinary Clinic, Nebraska
Casal J. et al. (2007) carried out a study of the factors associated to the collective medications in the compound feed or the water.
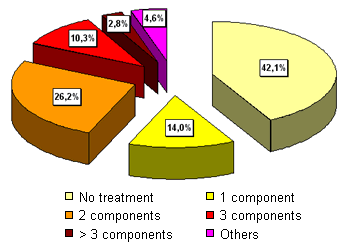
Therapeutic use of antimicrobials against digestive processes (%) according to the number if components used
n=107 (fattening farms); pigs/farm = 1,000 (60-3,800); Mortality = 5% (1-12%); Area = Catalonia
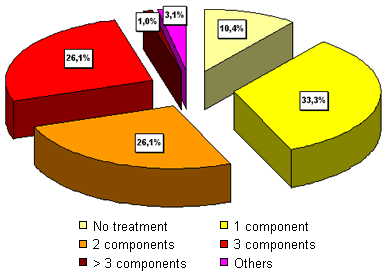
Therapeutic use of antimicrobials against respiratory processes (%) according to the number of components used
n = 107 (fattening farms); pigs/farm = 1,000 (60-3,800); Mortality = 5% (1-12%); Area = Catalonia
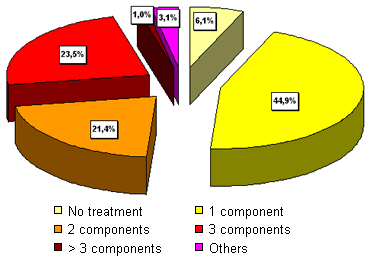
Prophylactic use of antimicrobials (%) according to the number of components used
n = 107 (fattening farms); pigs/farm = 1,000 (60-3,800); Mortality = 5% (1-12%); Area = Catalonia

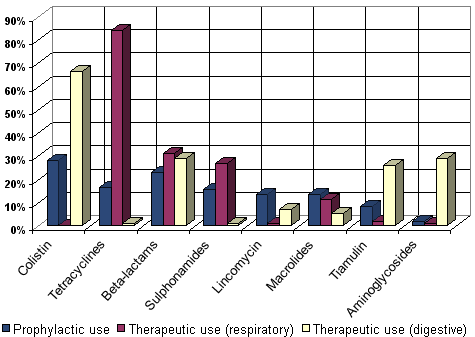
Use of the main antimicrobial products (%) in the collective prophylactic and therapeutic treatments (respiratory and digestive)
n = 107 (fattening farms); pigs/farm = 1,000 (60-3,800); Mortality = 5% (1-12%); Area = Catalonia
Casal J. et al. (2007) Vet. Res. 38 (2007) 481–492
There is a real danger of an uncontrolled increase of the "more or less therapeutic" collective medications associated to various components, and unsustainable from a health and economic point of view.
|
Goal: The health of the pig as a measurement of the welfare. |
There is always been a controversy between swine production, diseases and antimicrobial products because, on one hand, we must act against the diseases, but the management must be economically sustainable and give a good commercial image in front of the public health.
... in the collective medications we treat ill as well as healthy pigs.
Is it worth to fight against EVERYTHING with antibiotics?
The big farms are more prone to treat whole rooms instead of doing it individually or pen by pen. This can contribute to create resistances.
We must set out the treatments from the point of view of the business, according to the price of the meat (investment) and the production cost (efficiency) in order to improve the competitivity.
Expenses in drugs (a) and total cost of the piglet (b) according to the stage in normal commercial conditions in Spain.

The medication costs are low in comparison with the feeding or the fixed costs, but we must bear in mind the negative effects (direct and indirect) that can be created by a bad use, not only trebling the medication costs, but also many other things...
| Production data and medication expenses in piglets with a bad health in the fattening stage (annual, 2002) | |
| Pigs entered | 18,000 |
| Weight at entrance | 20 kg |
| Final weight | 104 kg |
| Mean number of origins | 13/farm |
| CI | 3.2 |
| Daily Live Weight Gain (DLWG) | 606 g |
| Mortality | 8.5 % |
| Total medication/pig | 7.17 € |
| Medication in the compound feed/pig | 3.86 € |
| Medication in the water/pig | 2.68 € |
| Individual medication/pig | 0.63 € |
|
Goal: Global economic control of the disease. Direct indicator: Use of drugs and strategy (diagnosis, product, dosage, frequency, administration route, etc.). Indirect indicator: Consequences of a bad use (mortality, DLWG, CI, etc.). |
10 items for the efficient approach of medications in the water:
1. Control all the CRITICAL POINTS (see last chapter).
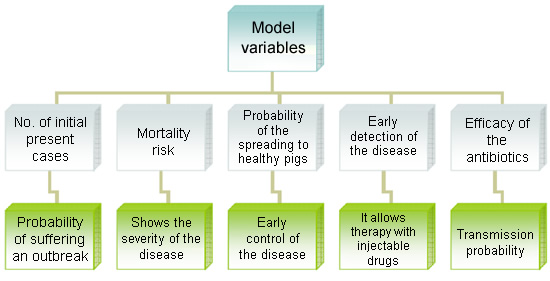
2. Apply epidemiological models for the RISK ANALYSIS/COST/BENEFIT.
The goal is to incorporate an effective treatment bearing in mind the number of ill pigs and the probability of their detection for their treatment. We must estimate:
- The behaviour and the magnitude of the disease in the sensitive population.
- The running of a program for the control of the disease.
4 epidemic curves (Haemophilus parasuis) according to the therapy used.
Number of cases per day with an initial prevalence of a 0.5%
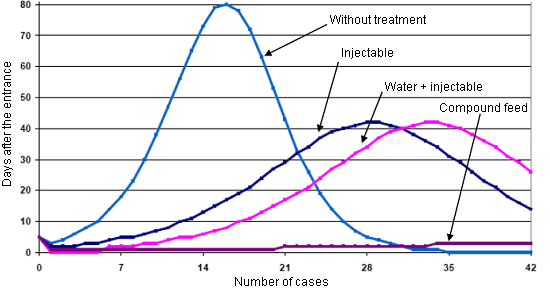
Morrison, R. and Deen, J. 2003. Proc. Leman Swine Conference (243-247)
Establish disease outbreaks "predictors" in order to be ahead and justify the use of antibiotics according to the dynamics of the disease. Assess the effect of the transferability over the financial value of the option:

The transmission probability by means of the Effective Contact rate (ECR) is the key factor that influences the epidemic curve to respond with medication. If the frequency is low, we will have to choose the individual injectable treatment, and if it is high we will carry out a collective treatment in order to offer a better financial return.
Example of the REED-FROST model
Ct+1= St * (1 - qct)
Where:
t = period of time
Ct+1= infected animals during period 1
St = sensitive animals during period t
q = 1-p = probability of an individual avoiding an effective contact, where p = K/(N-1), and K is the number of effective contacts.
3. Rational use of antibiotics:
It does not consist of stopping using them, but to use them correctly. We must understand the pharmacokinetics of the antimicrobial drugs and relate them to the pharmacodynamic effect in order to attain a clinical recovery as well as a bacterial elimination. The integration of both will carry us towards an efficient medication.
Pharmacokynetics according to its administration (injection and oral through the water and the compound feed):
Pharmacokynetics of an antibiotic according to its administration (injection or oral through the water and the compound feed)
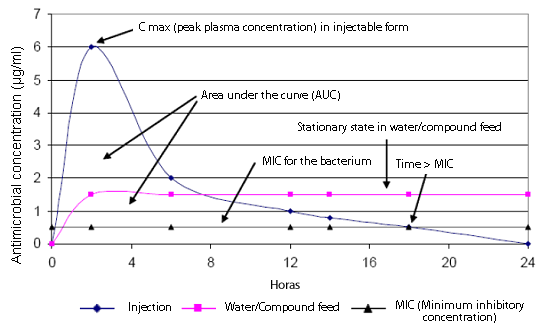
David G S Burch. Octagon Services Ltd, Old Windsor, Berkshire, UK
The antibiotics that depend on the time and the concentration are called co-dependent:
Example of the pharmacokynetic/pharmacodynamic relationship for enrofloxacin and Pasteurella multocida (MIC 0.03 μg/ml) (Lees & Aliabadi, 2002)
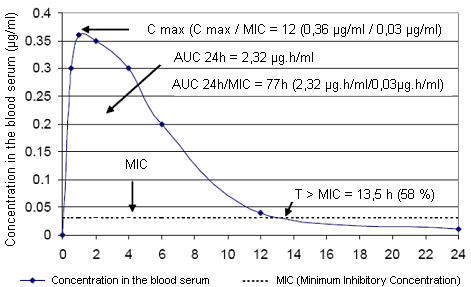
David G S Burch. Octagon Services Ltd, Old Windsor, Berkshire, UK
In pharmacodynamics we must know the sensitivity data of the most important pathogens against the antimicrobials.
Diameter of the inhibition area and MIC (Minimum Inhibitory Concentration) for tiamulin and A. pleuropneumoniae (Casals et al., 1990)
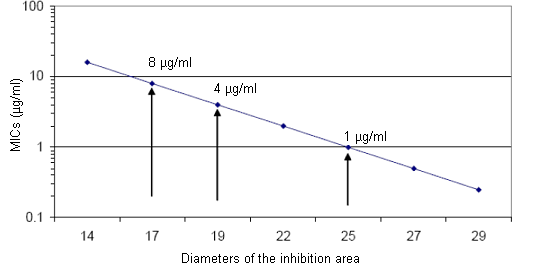
David G S Burch. Octagon Services Ltd, Old Windsor, Berkshire, UK
4. Quick return of the investment in medications.
Financial analyses are necessary in order to identify and monitor areas in which there is an opportunity cost, from the production system to the monthly monitoring of the drug consumption.
5. Correct sanitary management of the farm.
Improve health with actions at a global level (treatment, prophylaxis, biosafety, etc.) by means of a sanitary surveillance system carried out by a veterinarian in charge of it. Each farm must have its program and update it in order to adapt it to the real situation.
6. Financial evaluation of the problem: eradicate or control?
Sometimes, the eradication of a disease is not bearable. It will depend on the percentage of success of the implemented protocol, the financial benefit of the elimination of the disease, the financial benefit although the protocol fails, the reinfection index, the cost of the reinfection, etc.
Favourite methods for the eradication depending on the disease
| Depopulation - repopulation | Closing of the farm (3 sites) | Partial depopulation (Site 2 and 3) | Medicated early weaning (SEW) | Medication and partial repopulation only animals > 10 months old (Swiss method) | |
| PRRSv | ***** | **** | ** | ** | *** |
| Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae | ***** | ** | * | *** | *** |
| Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae | ***** | * | * | *** | * |
| SIV | ***** | **** | **** | *** | **** |
| Rinitis | ***** | * | * | *** | * |
| H. parasuis/S. suis | * | * | * | * | * |
| PCV2 | * | * | * | * | * |
For instance, the cost due to a poor performance and the treatments is fixed at 10.83 $/pig, and the investment in the depopulation and repopulation cost (10.02 $/pig), and the cost of the interrupting of the production (2.67 $/pig). (Paul Yeste, 2002 IPVS).
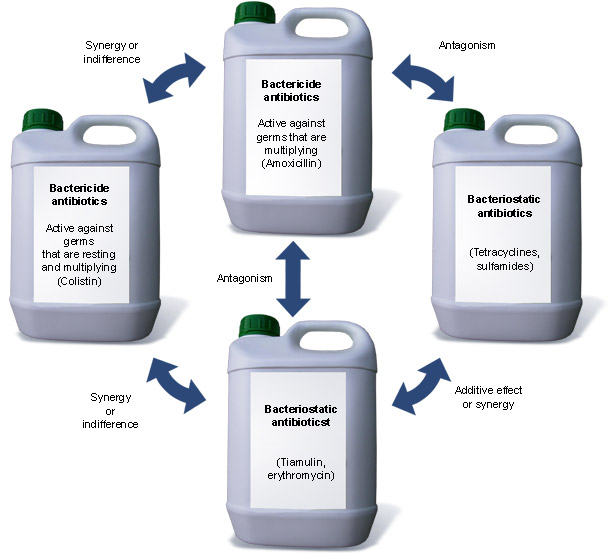
7. Seek the synergic effect when making antibiotics associations:
The nature, solubility and stability of the molecule is important (see chapters 1 and 7), but we must also bear in mind their action mechanism: bacteriostatic (they stop) or bactericide (they destroy). According to Jawetz's law, when mixing antibiotics there can be an "indifference" (sum of the action of both effects), "synergy" (the effect is higher than the sum of both antibiotics on their own) or "antagonism" (the effect is the inhibition of both).
8. Savings not attributable to the medications or the preventative strategies:
Act, if necessary, on the handling (All in/All out, avoid the mixing of pigs from multiple origins, etc.), census (structure, sanitary origin structure, etc.), installations and environment (density and volume/pig, airing system, etc.), genetics, feeding, etc.
9. Improvement of the farm in order to choose the best medication option (see chapter 6).
10. Strategic medications in the water:
- “Metaphylactic”: Apply treatments being ahead of the beginning of the disease. We must identify the specific pathogen and know the incubation period in order to establish the medication moment.
- “Pulsatile”: A cheaper alternative than the continuous medication in order to control diseases. Medicate in short periods (48-72 h) alternating with resting periods (96-120 h).
- “Continuous”: The pigs are medicated continuously during the critical periods of disease and bad health. We must check the management items before incurring the medication costs.
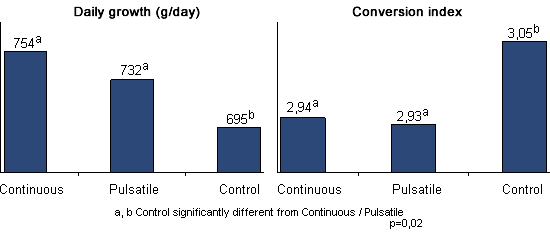
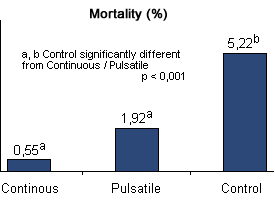
Comparison between pulsatile, metaphylactic and continuous medication on the health and the performance of the fattening pig affected by endemic respiratory problems:
| n = 1,092 | Week | |||||||||||||||
| Treatment | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 |
| Continuous | - | T | C | T | C | C | T | C | C | T | C | C | T | - | - | - |
| Pulsatile | - | T | - | T | - | - | T | - | - | T | - | - | T | - | - | - |
| Control | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
T: Tiamulin + Chlortetracycline (CTC)
C: Chlortetracycline (CTC 100)
-: Without treatment
 |
|
Walter D. et al. (2000). Swine health and production. Vol. 8 nº 2 pp 65-71
Both medication strategies improved the performance significatively in comparison with the controls without medication, but the pulsatile medication with the correct antimicrobials improves, also, the active immunity against the enzootic pneumonia.






