BM every 5 weeks with weaning at 28 days
What occurs is that the reproductive system is drawn out to 21 weeks, which isn’t wholly divisible among 4 lots every 5 weeks. In this situation, 3 batches remain with an interval of 5 weeks between them, while the 4th batch gets delayed to 6 weeks.
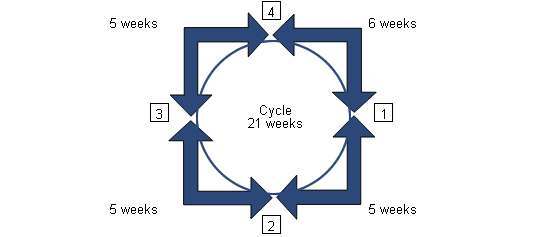
In this case, the distribution of traditional weekly BM tasks would be altered as followed:
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 |
| W | M + B |
0 | 0 | 0 | W | M + B |
0 | 0 | 0 | W | M + B |
0 | 0 | 0 | W | M | B | 0 | 0 | 0 |
M = Mating
B = Births
0 = Nothing
- The births join up with the matings throughout 3 lots.
- In the 4th lot, the tasks are organized in a “traditional” manner (one week for each main activity).
- With this “alternative” BM system, we have been able to fill part of the “emptiness” that we came upon in the last chapter. No we can take advantage of the 5-week maternity rotation time in order to wean at 28 days.
- This option is probably ideal for small-medium sized farms. However, on larger farms we come upon the problem of excessive task grouping. What can we do in these cases?
| Farm 1: | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| W | M + B |
0 | 0 | 0 | W | M + B |
0 | 0 | 0 | W | M + B |
0 | 0 | 0 | W | M | B | 0 | 0 | 0 | W | M + B |
0 |
| Farm 2: | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 1 | 2 | 3 | |||
| W | M + B |
0 | 0 | 0 | W | M + B |
0 | 0 | 0 | W | M + B |
P | 0 | 0 | 0 | M | B | 0 | 0 | 0 | |||
| Farm 1+2: | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| W | M + B |
0 | W | M + B |
W | M + B |
0 | W | M + B |
W | M + B |
0 | W | M + B |
W | M | B | W | M | B | W | M + B |
0 |
When joining the weekly tasks from both farms, the distribution of activities would be as shown in this chart. We would have 3 cycles of 5 weeks (beginning with weaning, marked in blue) with one distribution: Weanings / Matings+Births / Nothing / Weanings / Matings+Births
Following would be 2 lots with a 3 week rhythm between each batch: Weaning / Mating / Births.
The orange square marks the start of a new sequence, exactly identical to the one described.
Now, lets imagine that the 2 farms that were out of turn are now organized within the same farm. It would be a fusion of 2 BM systems every 5 weeks with weaning at 28 days that would generate a 3-2 BM system with weaning at 28 days.
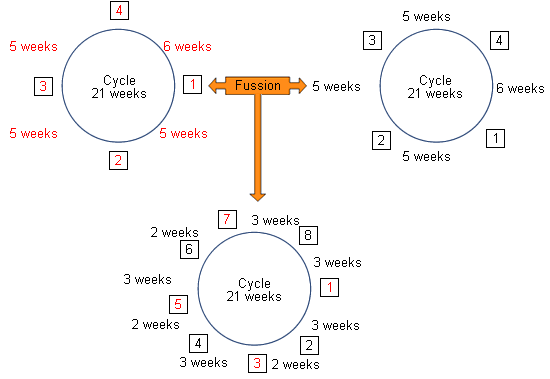
1.
Allows what we have been looking for from the beginning: Rotation every 5 weeks, weaning at 28 days:- The 5 week rotations are no longer exclusive territory of 5-week BM systems.
- This opens the door for BM systems on mid sized, and even large farms (more than 1000 sows).
2.
Higher productive capacity than the 3 week batches, but still weaning at the same age (28 days):We are able to achieve 1 productive lot more than in the case of 3 week batches.
- BM every 3 weeks: 7 productive lots
- BM every 3-2 weeks: 8 productive lots
3.
As with the 3-week BM system, the sows that are delayed 1 week can be reincorporated, weaning them at 21 days in the next cycle. However, with the advanced sows, there isn’t as much of a margin.4.
Allows for a greater margin when surpassing the forecast farrowings than the BM system every 2, 4, and 5 weeks.5.
Repetitions at 21 days tally well with the next lot: On occasions exactly, and other times there is a 1-week delay.6.
Greater ease when making fostering sows than with other BM systems.7.
Good task distribution:- Matings and births within the same week.
- Weanings do not coincide with births.
- One “free” week out of every 5.
8.
Possibility of working with irregular batches: when disposing of an even number of lots (8) the possibility of working with lots that have a different number of sows exists. For example, if we have 120 maternity slots available, we would look for 70 births in one lot, and 50 in the next. This aspect is compromised in the case of 3-week BM system because with an odd number of lots (7), when weaning a lot with fewer sows (50), it should become a lot with more sows (70), and vice versa.Disadvantages:
This can seem like a more complicated system, since there is no constant weekly task distribution, but once installed, the only aspect to keep in mind is that we have to wean when the lot reaches 28 days. And even so, it is highly recommendable to use a mating schedule so as not to loose track.
If we have time in gestation – control for 2 lots (5-week rotation), we should move sows to confirmed gestation (yards, with the new welfare law) for 30 days. Another option is to have space for 3 gestation- control lots and move them at 35 days. We will have empty pens during 1-2 weeks, but all the same, this extra space is necessary to be able to move the sows to be weaned.
Aspects to keep in mind:
If in the transition we have space for 2 lots of piglets, we will have 4.5 weeks of housing (1 less than with a 3-week BM system).
If we have space for 3 lots, one lot will have 6.5 weeks of housing and then next will have 7.5 weeks.
This situation will be altered when the 2 lots that are 3 weeks apart arrive, becoming level with the 3-week BM system situation.





