Assays available:
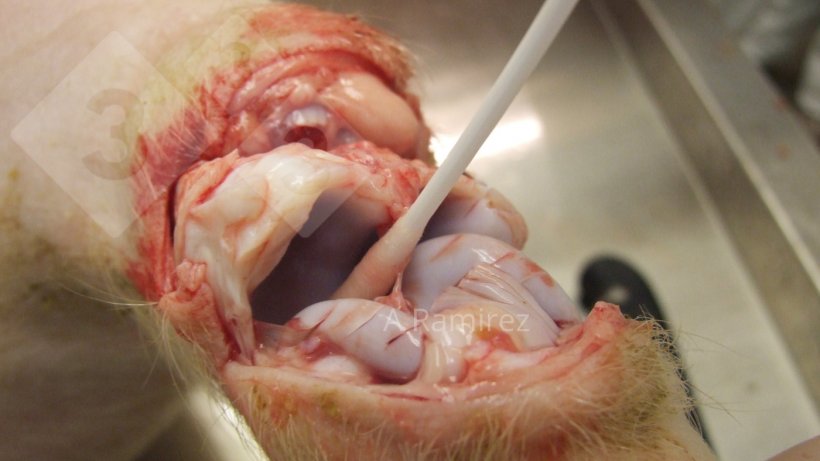
Gross pathology

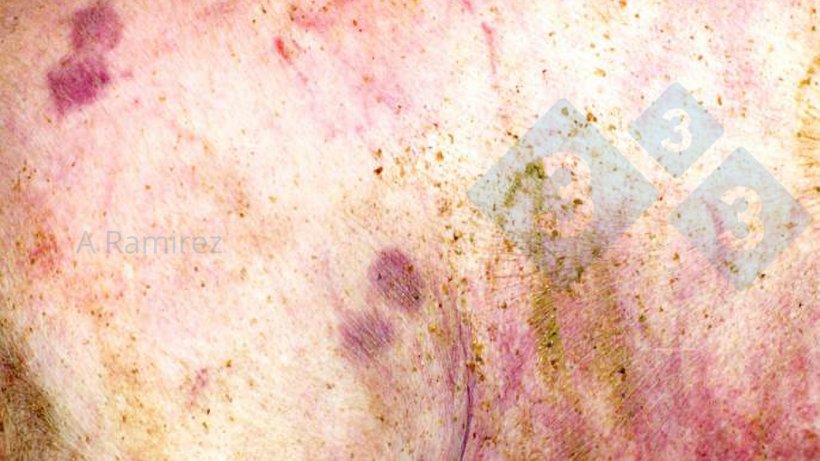
- Visual inspection of lesions
- Pros:
- Almost pathognomonic: Acute skin lesions (slightly raised), multifocal pink to purple diamond-shaped lesions
- Cons:
- Other than skin lesions, all other lesions are common to many other diseases
- Usually require other diagnostic confirmation
Bacterial culture
- Isolation of live organism from tissues with lesions
- Sample types: blood, spleen, lung, liver, kidney, lymph nodes, joint fluid
- Pros:
- Bacteria is easy to grow in 1 or 2 days for acute cases
- Easy to do in any lab (including in-house)
- Relative low cost
- Cons:
- Selective enrichment may be necessary for chronic cases
- Bacterial growth can be prevented in samples from pigs previously treated with antibiotics
Antimicrobial susceptibility
- Tests in vitro ability of live organism to grow under specific concentrations of different antimicrobials
- Sample types: blood, spleen, lung, liver, kidney, lymph nodes, joint fluid
- Pros:
- Identification of susceptibility or resistance of specific isolate to common antimicrobials
- Identification of antimicrobial resistance trends
- Cons:
- Requires a bacterial isolate
- In vitro testing may be slightly different than in vivo results
- Some specific antimicrobials may not be tested or require separate, special testing
- Moderate cost
Immunohistochemistry (IHC)
- Detects presence of bacterial antigen
- Sample types: tissues
- Pros:
- Detects bacteria at site of lesion (good proof of causation)
- Can be useful in chronic cases or when animals have been treated with antibiotics and bacterial culture can be challenging.
- Cons:
- Correct tissue sample must be submitted
- Requires significantly more bacteria to be present than PCR
- Only evaluating a small tissues sample
Polymerase chain reaction (PCR)
- Detects presence of specific sequence of bacterial nucleic acid (DNA)
- Sample types: tissues, whole blood, serum, oral fluids, etc.
- Pros:
- Very high sensitivity (can detect small amounts of bacteria)
- Many different sample types can be used
- Moderate cost
- Cons:
- Cannot differentiate live vaccine bacteria vs. wildtype infection
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA)
- Detects presence of antibodies
- Sample types: serum
- Pros:
- Animals can remain positive for many months
- Antibody level in many assays correlate well with protection
- Can be used in chronic cases
- Cons:
- Specific antibodies detected and timing of detection may vary slightly between the different commercial kits available
- Many healthy pigs can be carriers and test serologically positive
- Unable to differentiate maternal antibodies vs. exposure
- Unable to differentiate vaccine vs. wildtype infection
Result interpretation:
Gross pathology:
- Positive: Skin gross pathology can be used for presumptive diagnosis
- Negative: Chronic cases usually don’t manifest with skin lesions
Bacterial culture:
- Positive: Confirmatory of disease
- Negative: Negative, or may need enrichment especially in chronic cases or testing is done late after infection
Antimicrobial susceptibility:
- Susceptible: possible good choice for treatment if antimicrobial can reach target tissue
- Resistant: select different antimicrobial
- MIC: MICs are done to ensure that the antimicrobial selected achieves the listed MIC value in the target organ
IHC
- Positive: Bacteria is present at site of lesion
- Negative: Negative, or bacteria could have been missed if testing occurs late after infection or after antibiotic treatment
PCR
- Positive: Bacteria is present/circulating and confirms disease. Recent vaccination with a modified live vaccine can result in positive PCR results.
- Negative: Negative, or bacteria could have been missed if testing occurs late after infection or after antibiotic treatment
ELISA

- Positive: Maternal antibodies or past exposure (usually > 7-10 days post exposure) to vaccine or wildtype virus
- Negative: Negative, or infection too early to detect (usually takes 2 to 4 weeks post exposure)
Scenarios
- Pigs with skin lesions (usually > 20 kg):
- Confirm gross lesions as true “diamond-shape” for a presumptive diagnosis
- Collect spleen or liver from any dead pigs or collect blood sample from live pig for bacterial culture
- If pigs have been treated with antibiotics, request culture via selective enrichment
- Chronic arthritis (usually > 20 kg):
- Collect joint fluid from affected pig(s):
- Individual PCRs
- Culture via selective enrichment
- From dead pig(s) also collect synovium and affected cartilage for Erysipelas IHC
- Collect joint fluid from affected pig(s):