Description of the farm
Factory farm with 1,500 producing sows in two sites located in Mexico.

- It weans the piglets when they are 19.5 days old.
- The pigs are marketed when they are 146 days old and they weigh 113.7 kg (averages).
- The mortality in the weaners and the fattening periods is low: 0.7% and 1.1% respectively.
- They wean 26.8 piglets / sow / year.
The production results are good, but the mortality in the farrowing quarters is high, and it is even higher during the hot months (from July to September), when it exceeds a 12%.
The installations are simple, with open buildings and some closed farrowing quarters, with a wet wall.
The farm is free from the main diseases of swine in Mexico: PRRS, Aujeszky's disease, Classical Swine Fever, App, mycoplasma, etc.
Appearance of the case
In July, when the temperature and the relative humidity had risen, there was a considerable mortality increase in the farrowing quarters that went from an 11.7% during the previous weeks to a 24.6% during the week with the highest mortality.
The main causes of mortality were: crushed piglets (41.1%), undernourished piglets (23.7%), diarrhoea (9.2%), piglets born with a low weight (8.0%), euthanized piglets (6.8%), splayleg (5.2%) and pneumonia (1.4%).
As it can be seen, the majority of the causes were due to handling errors. With regard to the symptoms, only diarrhoea and pneumonia were seen.
Diarrhoea increased since 7 weeks before, until it affected more than the 50% of the litters of less than seven days of age. Seemingly, it was caused by E. coli and it was associated to the temperature and relative humidity increases.
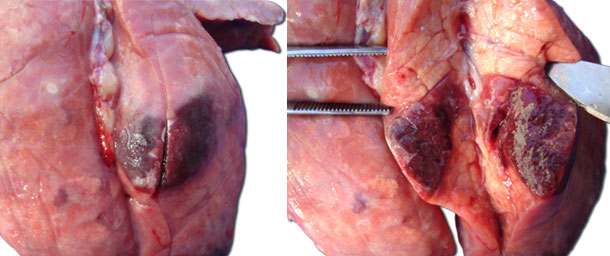
Image 1. Acute local pleuropneumonia. The lung collapses.
During the previous 4 weeks the number of piglets that died due to pneumonia increased. The pneumonia lesions were very severe and the worry was that an Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae (App) outbreak was starting in the farrowing quarters. This farm was depopulated 1.5 years before due to App in the fattening stage and the wish was to confirm the diagnosis.
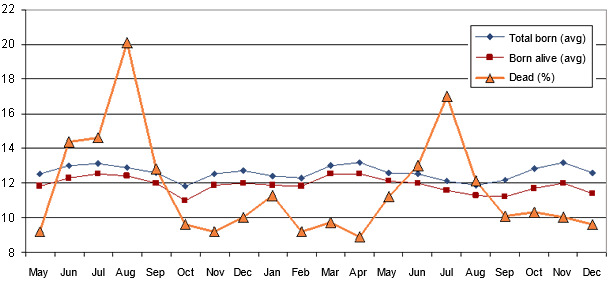
Graph 1. Total piglets born, born alive and mortality in the farrowing quarters

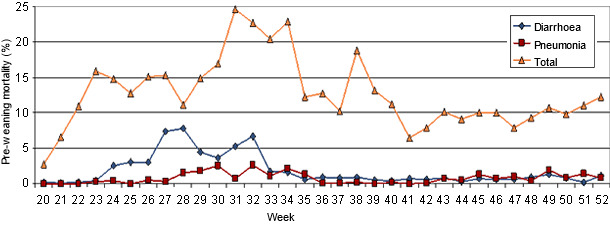
Graph 2. Mortality percentage in the farrowing quarters
Causes of mortality in the farrowing quarters
| Crushed | 41.1 % |
| Starvation | 23.7% |
| Diarrhoea | 9.2% |
| Low viability | 8.0% |
| Euthanized | 6.8% |
| Splayleg | 5.2% |
| Pneumonia | 1.4% |
| Others | 3.8% |
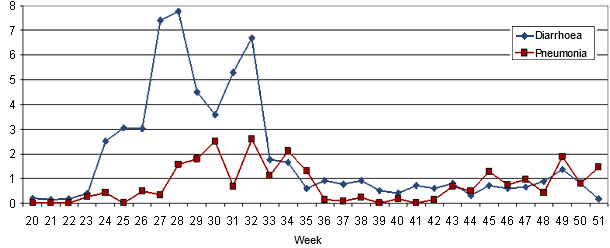
Graph 3. Mortality percentage due to diarrhoea and pneumonia
Visit to the farrowing quarters
Environment:
The farrowing quarters were very hot and damp. The temperature was 32ºC in the closed rooms and 38.5ºC in the open rooms. A high relative humidity was perceived in the environment (it was not measured due to the lack of a device, but apparently it was >80%).
Clinical signs:
- The females were OK, but their feed consumption dropped due to the heat. They did not get up to eat, and many of them lost body condition (more in the open rooms).
- Diarrhoea was seen in several litters (20%) during their first days of life.
- In the 4- to 7-days-old piglets we saw that some of them were weak, a bit pale, down, with fever and a slight dyspnea.
- The number of crushed piglets remained high, especially during their first 3 days of life.
- At 9-10 days of life we saw several thin and undernourished piglets.
Handling:
There were deficiencies in the handling of the piglets:
- They gave 24 hours (or less) for the cleaning and disinfection of the rooms.
- The environment and the floor of the rooms was damp.
- Hygiene was lacking in some rooms.
- They transferred piglets of the majority of the litters. They made too many transfers.
- More than the 30% of the litters had a nurse sow.
- They weaned the litters when they were 10 days old, and the sow was used as a nurse sow.
- The handling of these piglets was poor: they were not taught to eat and drink and they lacked a heat source.
Treatments:
- At birth all the piglets received citric acid at a 20% concentration orally to treat diarrhoea and they were injected vitamins.
- At 4 days of age the piglets received toltrazuril orally.
- The drug was administered with the pigs upside down (belly up).
- They did not give enough time for the piglet to swallow.
Necropsies:
- Fibrin in the visceral and parietal pleura.
- Trachea with haemorrhages, necrosis and abundant mucopurulent exudate.
- Presence of white lumps in the airways.
- Lung with lobular necrotic lesions covered with fibrin. Abscesses in some pigs.
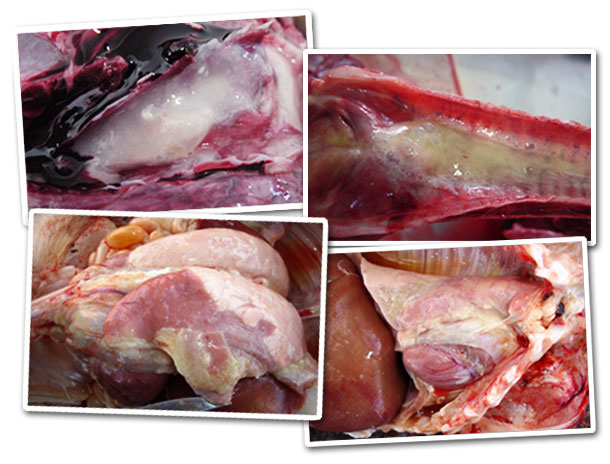
Image 2. Mucopurulent exudate in the trachea with unknown material white lumps.
Image 3. Mucopurulent exudate, with haemorrhages, in the trachea and larynx.
Image 4. Pleuropneumonia with abundant fibrin and abscesses in the parenchyma.
Image 5. Pleuropneumonia with abundant fibrin and liquid in the thorax.
Diagnosis
Necrotizing tracheitis and pneumonia due to aspiration was diagnosed.
The pneumonia problems in piglets are uncommon, so the finding of a pleuropneumonia similar to that seen in growing pigs and caused by Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae (App) is unlikely. App affects pigs normally between their 14th and 18th week of age. In piglets penumonia is very rare and, generally, it is not seen during their first week of life.
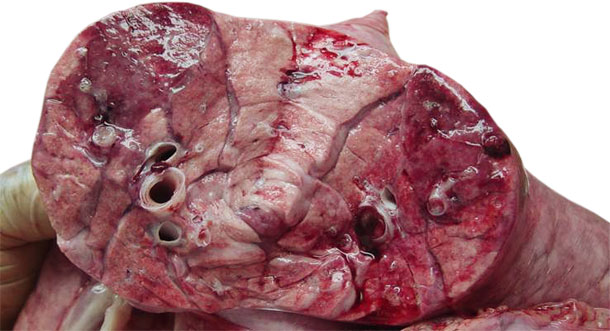
Image 6. Necrotizing pneumonia with abundant exudate in the bronchi and small abscesses.
Bronchoaspiration is common in farms in which oral treatments are given to the piglets, especially when the piglet is not put in a correct position and it is not given enough time to swallow. In this case it was confirmed that the handling of the piglets with diarrhoea was inappropriate and that the drugs and milk went to the trachea and the lungs.
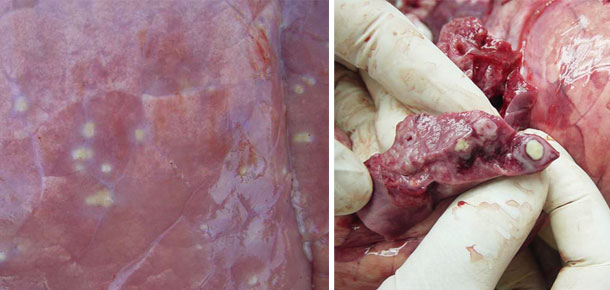
Image 7. Necrotizing pneumonia with abscesses.
The treatment with toltrazuril was not recommended, Isospora suis was not found and diarrhoea due to coccidia appears after 7 days of life. Also, the product is very acid, and when entering the trachea and the lungs it causes necrosis.
Recommendations:
Treatments:
- Suspend the oral treatments for the moment until the staff is properly trained.
- If oral treatments have to be administered, they should be given with the pig with its legs down and giving it time to swallow.
Diarrhoea control: Handling:
- Verify that all the piglets suckle colostrum.
- Improve the hygiene in the rooms. Reduce the dampness on the floors.
- Clean and disinfect when the room is still damp and leave it to dry perfectly until the entry of the next group of sows.
- Let the rooms "rest" (stay empty) for more days.
- Bathe and disinfect the sow before entering it in the farrowing quarters.
- Avoid temperature changes for the piglet.
- Reduce the movement and the handling of the piglets. Transfer only those that have to be transferred.
- Apply the vaccine against E. coli to all the first parturition sows at the 80th and 100th day of gestation.
- In this farm it is not possible to reduce the temperature in the farrowing quarters. Modify the ventilation. Use plastic pipes with a fan and water dripping.
- Put a wet wall.
- Put insulation on the ceilings.
- Block up all the holes through which hot air enters.
- Control the feed consumption of the sow in the farrowing quarters.
Final comments
- The problem was considerably reduced when the oral treatment against diarrhoea was suspended.
- But some cases of broncoaspiration were still seen. In a later visit it was seen that they gave colostrum orally (or by oro-nasal tube) as a routine to weak piglets or to piglets with a low weight without verifying if the tube was in the stomach.
- It is confirmed that the staff training programs must be continuous.






