Farm introduction
The farm in this case study is a large integrator farm located in the wide-open plains and arable lands of Romania in south-eastern Europe. The farm system was established several years ago, in older communist-era buildings that had been adapted for modern breeder pigs. The owners then financed and organised additions of several large grow-out sites, built by major farm building construction companies. The breeder farms had been stocked with 10,000 gilts of British breeding company origin. These pigs were bred with 20 percent Chinese Meishan input, so they had excellent temperament and mothering ability. In the past 5 years, further expansion was achieved via purchase of 2,000 more sows of German breeder company origin; these gilts had better growth and feed conversion characteristics, but were more excitable and aggressive.

Some of the breeding farm sites are positive for EU strains of PRRS, but some are negative. The farm uses piglet vaccines throughout for control of PCV 2b Circovirus associated diseases. The farm is positive for most diseases endemic in Europe, including swine influenza, Lawsonia, and swine dysentery.
Breeding sows and gilts receive commercial vaccinations against E. coli (fimbrial antigens K88 [F4], K99 and 987P), parvovirus, erysipelas and leptospirosis. Piglets are vaccinated at 2 weeks-old against Mycoplasma and porcine circovirus with commercial one-shot vaccines.
The farm system also has full integration with a large feed mill operation and a large modern slaughterhouse facility. There is therefore a multi-layer management set-up. Part of this set-up within the feed mill, has decided to fully implement some EU guidelines on feed additives.This means that they have recently reduced the in-feed dose of Zinc oxide added to the post-weaning starter diet to less than 200 ppm.
Wean-to-finish systems
Pigs are weaned from all gilts and sows at 24 days old. The large scale of this farm system means that each nursery site receives 2,000 weaned piglets per week. Each farm site is located in an isolated area, over 20 km away from other known piggeries. The farm has excellent purpose-built housing for these groups of wean-to-finish pigs, see Figure 1.
Emergence of the case
The pig farm management team in charge of the post-weaned piglet nursery areas on these wean-to-finish sites has found serious problems with diarrhoea in recent batches of piglets arriving from the breeding farms.

Figure 1. Typical new-build Eastern Europe weaner sheds in open arable areas.
The farm has a group of technical and veterinary experts assembled into a team approach.
On walking around the farm and the nursery pig houses, an inspection is made of their heating, sanitation and ventilation, and of pen and office charts to establish the mortality levels of each section of pigs. The team is directed to the affected pens, where some diarrhoea is evident on the floors of the pens (see Figure 2).

Figure 2. Watery yellow projectile diarrhoea in 5 week-old weaner pigs.

The team confirms clinically that numerous piglets, 7 to 14 days after weaning are displaying watery yellow projectile diarrhoea. The pigs remain reasonably alert, but an increase in mortality levels is noted.
The team collects some samples of this diarrhoea in affected nursery pens and also autopsy a few affected pigs with severe diarrhoea, and note the intestinal loops that are congested and dilated with watery yellow fluid, see Figure 3.
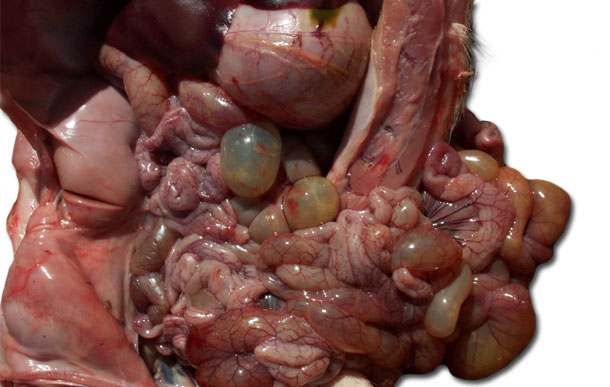
Figure 3. Autopsy of affected nursery pig, note loops of small and large intestine.
Some samples of fresh faeces and intestines were sent to the lab for testing. The differential diagnosis at this stage includes E. coli, Salmonella, PCV, Lawsonia, TGE, PED, rotavirus.
Some days later the team receive the results. In conversation with the lab, it is confirmed that culture of intestine samples on blood and McConkey agars show heavy pure growth of lactose-fermenting, indole-positive, oxidase-negative and beta-haemolytic colonies of Gm - coliforms. Agglutination reactions indicate fimbrialK88 [F4] ++ reactions typical of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli (ETEC).
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
 AA
AA
Veterinary Laboratories Agency
East Europe branch
Date Received 07/09/2010
Date of Sampling 29/08/2010
Case Vet
Species / Breed Porcine / LW Landrace
Sex / Age Mixed / 4 weeks
Samples Faeces x 10, Intestines X 4
23jd
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Report 1a and 2
| Species | Sample Ref | Site | Isolate | Isolate Ref |
| Porcine | 4 week old | Faeces | Haemolytic E coli spp | IS23-00173 |
| 4 week old | SI | Haemolytic E coli spp | IS23-00174 |
Sensitivity report added for the haemolytic E coli isolated from Animal 4 week old # 00174
Test Results: S - Sensitive R - Resistant
| Antimicrobial | Disc Content | Result |
| Apramycin | 15 µg | S |
| Spectinomycin | 25 µg | S |
| Neomycin | 10 µg | S |
| Amoxicillin / Clavulanic acid | 30 µg | S |
| Trimethoprim / Sulphamethoxazole | 25 µg | S |
| Ampicillin | 10 µg | S |
| Enrofloxacin | 5 µg | S |
| Tetracycline | 10 µg | R |
Lab notes:
- Organisms sensitive to neomycin are generally also sensitive to framycetin.
- Ampicillin and amoxicillin have similar activity.
- Enrofloxacin is chosen to represent the licensed fluoroquinolones (danofloxacin, marbofloxacin and enrofloxacin).
- In general cross-resistance exists between the tetracycline group.
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Analysis of results
The clinical signs, autopsy and lab results suggest that an entero-toxigenic Escherichia coli (ETEC) had colonised many pigs’ intestines shortly after weaning, causing typical cellular disturbances and watery yellow diarrhoea. The fimbrial E coli antigen vaccine usage among sows and gilts is aimed for lactogenic immunity against ETEC in neonatal piglets and does not protect against ETEC infections in post-weaned pigs – that is once the pigs stop consuming maternal antibodies.
The occurrence of clinical ETEC infections in post-weaned pigs had dropped away to a very low level since the 1980’s with the introduction of in-feed Zinc oxide at sufficient pharmaceutical levels (1,500 to 3,000 ppm) in early starter diets. Zinc oxide has a specific anti-bacterial action damaging and distorting bacterial membranes with leakage of bacterial contents. However, recent European legislation initiatives aimed at environmental cleanliness have served to limit its general use; these initiatives have now led to a reduction in its use on some farms.
On this case farm, the reduction of zinc oxide usage away from appropriate pharmaceutical levels quickly led to outbreaks of clinical ETEC infections.
Measures taken
The farm placed in-feed and in-water antibiotics indicated by the antibiotic sensitivity charts into the feed and water supply of starter pigs, to try to limit losses in mortality and lost production. Neomycin sulfate given at 100 ppm orally were used against ETEC in some of the outbreaks with little evidence of clinical recovery. Colistin is regarded by some as the drug of choice for ETEC therapy, with no clear indication yet of resistance among European isolates. However, the scale of the problem on this farm meant that dosing of all pigs in recurring outbreaks on a variety of wean-to-finish sites, each outbreak occurring over a 2 to 3 week period, was expensive and logistically difficult.
Zinc oxide was replaced back into the post-wean starter diets at pharmaceutical levels on veterinary prescription and the clinical signs and losses resolved within 2 weeks on all sites.
The clinical signs among some of the outbreaks suggested that vero-toxin (shiga-like toxin) positive strains of ETEC were also present in some farms.
E. coli and ETEC strains are a common background organism that is considered to be “embedded” in most pig farms, presumably in materials in the pens, walkways, slurry etc. This embedded nature explains its constant nature of occurrence and outbreaks when appropriate control measures are not taken.
Some progress has been made towards a useful vaccine for post-weaning ETEC problems, so the problem of restricted zinc oxide usage and antibiotic usage and the widespread nature of the disease can lend itself to the use of a vaccine approach in the future. For example, one current vaccine of Canadian origin is a pure culture of avirulent E. coli bacteria, without toxins. When administered to piglets, it binds to intestinal cells and triggers the animal's immune response. Antibodies rapidly multiply and prevent the colonization of pathogenic ETEC bacteria in the intestine.





