China accounts for about 50% of global pork consumption and has traditionally been China's most popular meat. China's pork consumption remained relatively stable, fluctuating between 53-55 million metric tons annually from 2013 to 2018. However, the ASF outbreak decimated the domestic pig herd in China, which led to a severe pork shortage in 2019. This caused pork prices to skyrocket, and pork consumption in China dropped significantly in 2019, declining by about 21% compared to 2018.
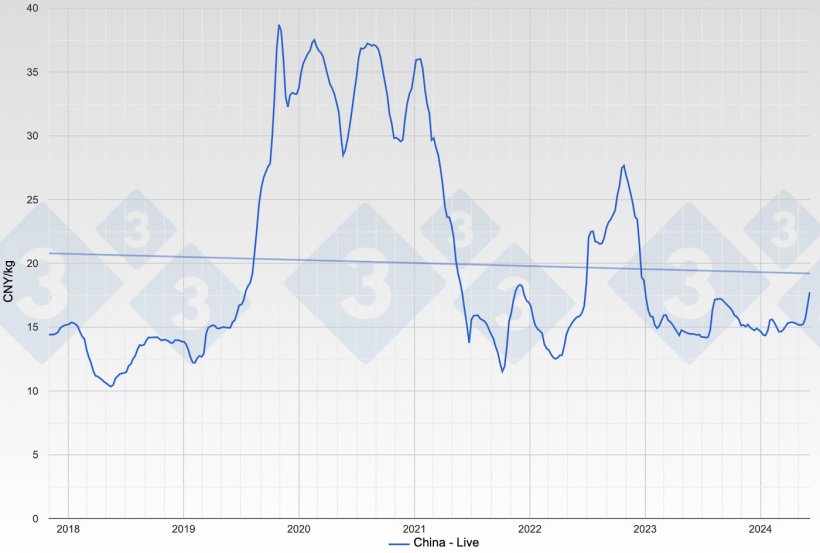

To keep pork available at a reasonable price, the Chinese government implemented various measures to rebuild the country's pig herd, including subsidies and restocking efforts. The pig producers and investors keep investing in swine industry for the incredible profit at that time. As a result, China's pork production and consumption have been gradually recovering since 2020 and the estimated consumption was around 48 million metric tons in 2021.
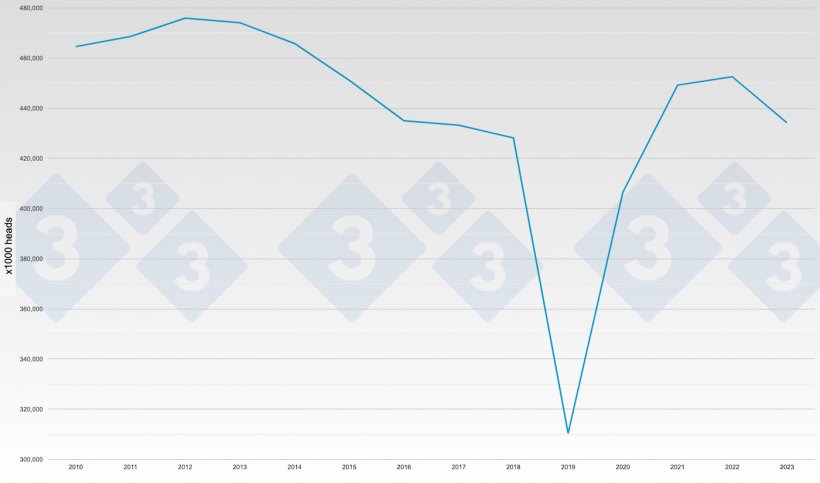
The trends of the swine industry in China will be explained in two parts: pork consumption and pig production.
Pork consumption declined to a relatively stable level
- Newborn population decline. The newborn population declined from 15.23 million in 2018 to 9.02 million in 2023, which is still ongoing. Young couples without children tend to cook less but consume more takeout food with alternative protein sources. This big drop in the newborn population influences the overall demand for pork at the household level. With a declining number of children in schools and other institutions, the overall demand for pork in these settings may decrease.
- Older consumer preferences. Older consumers may have different pork consumption habits, potentially favoring lean meat or seeking alternative protein sources like poultry products that are perceived as healthier. Moreover, fish and seafood are becoming popular as alternative protein sources in China. All these alternative protein sources will definitely replace certain demand for pork.
- Income and Urbanization. The growth of income and the expansion of the middle class will lead to increased purchasing power, which can drive higher demand for pork and other protein sources. Consumers in urban areas may have a willingness to pay for higher-quality, premium pork products. For example, the Huateng company located in Zhejiang province provides high-quality pork of local black breed pigs and is gaining popularity among middle-class families.
Pig production: the productivity level of China's pig industry keeps improving
- Biosecurity improvement. ASF is still the main concern of pig producers and makes the producers and professionals feel a stricter biosecurity system is the majority method to decrease the risk of ASF outbreak. Unlike before 2018, many pig producers did not take biosecurity seriously. Therefore, the frequency of other severe disease outbreaks is also decreased accordingly.
- Health management improvement. Partial depopulation especially test and removal method is still the main way to minimize the loss of ASF outbreaks even though there are different strains of ASF reported in China. Thus, walking the pen to find the pigs with abnormal clinical signs and test for ASF is one of the most important daily works in pig farms nowadays. The sick pigs will be culled instead of keeping them in the farms like before.
- Technological advancements and the adoption of new farming techniques. The batch production system including weekly batches, 3 weeks batches, and 4 weeks batches is well accepted and adopted in pig farming to achieve all in/all out. Moreover, Boar odor products to stimulate the sows are popular with farms in high ASF risk areas to avoid the ASF spread on farms by snout contact between boars and sows. The air filter ventilation system has started to be installed on pig farms to minimize the risk of ASF spreading via airborne.
- The good genetic potential of breeding pigs. Because many breeding stocks were depopulated after the ASF outbreak, many producers in China had to keep old genetics, zig-zag sows, and even female finishers as breeding sows. As their management level increased, more and more pig producers had strong needs to replace their own genetics by better genetic potential as breeding pigs. Therefore, many breeding companies imported breeding animals from Denmark, France, the Netherlands, Canada, the US, etc. These good genetics will enable the pig producers to improve the production potential.
- Productivity increased but the sow inventory decreased. the number of market pigs per sow per year (MSY) has kept increasing from 15.98 in 2021 to 17.11 in 2023, and the sow population decreased from 43.51 million in 2021 to 42.48 million in 2023 accordingly. The sow inventory will keep decreasing as the increasing productivity and the consumption of pork remain at a relatively stable level.
- Production costs decreased to improve the margin of pig farming. The skyrocketing pork prices attracted pig producers and investors to invest to build many new farms in the past, making many pig producers in China have high debt ratios generally. However, the profit of China's pig industry has been extremely low for a long time which puts the pig producers who have high debt ratios under heavy pressure to keep the cash flow return positive. Some estimations said the current sow population only achieves about 70% of the total pig production capacity in China. This means many producers and investors who invest in pig farms may have very rare or even no income. As a consequence, 3 of the top 10 producers in China are experiencing reconstruction.
In summary, the swine industry in China is experiencing the challenge of pork consumption declining and the overcapacity of pig farming. Pork consumption is influenced by population aging, customers’ preferences shifting, and economic development. The trend of improving pig farming productivity by adopting a biosecurity system, good health management, advanced technology, and good breeding animals will decrease the total sow population and production cost.



