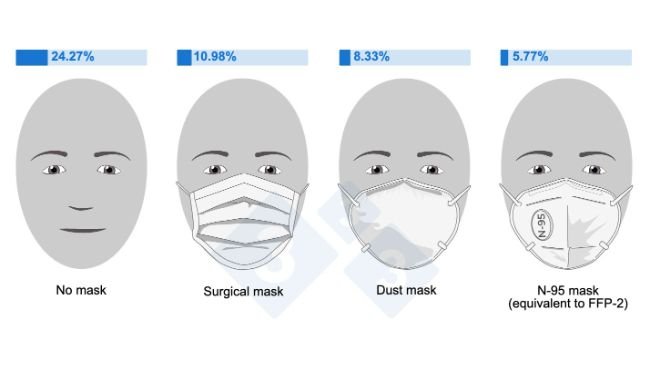
Influenza: The value of implementing simple measures consistently
Breaking the chain of infection from humans to pigs and from pigs to humans.
The pig sector events all around the world
Weekly newsletter with all the pig333.com updates
Swine industry news in your email
Pig health: news and articles on PRRS, PCV2, biosecurity, etc, Pig disease guide, atlas of pathology, clinical cases…
Biocheck.UGent is an independent, risk-based, scientific scoring system for assessing the quality of your on-farm biosecurity.
A visual and practical step-by-step guide on how to perform a necropsy on a pig.
All the information about ASF: how to recognize the disease, how it is transmitted, pictures of lesions, latest news, guides, etc.
All the information on Foot and Mouth Disease in pigs: how to recognize the disease, how it is transmitted, images of lesions, latest news, guides,...
Description of the most important diseases and conditions in pigs
Images of major swine diseases
Pig disease diagnostic tool
Definition for the most commonly used pig terms
Simulator that calculates the amount of drug to add to the water when using a flow dispenser.
Weekly newsletter with all the pig333.com updates
Pig Prices by countries. Pork production and trade. News of the pig market and the raw materials
The latest slaughter pig prices in the most important pig markets. Check the evolution of the historical prices in charts and in several currencies.
Latest quotations for the main commodities used in pig feed. Historical graphs with the pig price and estimated feed price.
Figures & trends in pig numbers, pork production and pork trade.
Global production and trade data for the most important raw materials
Weekly newsletter with all the pig333.com updates
Articles on nutrition and pig feeding, characteristics of raw materials and additives for pig feed. Prices of raw materials
Latest quotations for the main commodities used in pig feed. Historical graphs with the pig price and estimated feed price.
Technical sheets of the main raw materials and additives used in swine feed. They include a comparison of nutritional values from various sources, product
Global production and trade data for the most important raw materials
Definition for the most commonly used pig terms
Use this tool to diagnose problems with the feed conversion ratio. Click on the flowchart or on the buttons within the text to navigate through the different parts of the tool.
A biweekly newsletter with the latest developments in swine nutrition
Articles on genetics and pig reproduction: genetic improvement, genomics, artificial insemination, use of hormones
Compare production data, calculate the number of sow, nursery, and finishing spaces, and visualize your tasks on the work schedule by type of BMS.
Tool that allows you to calculate the replacement rate in your farm
Definition for the most commonly used pig terms
Use this tool to find out why your farrowing rate is less than ideal. Click on the flowchart or on the buttons found within the text to navigate through the different parts of the tool.
Weekly newsletter with all the pig333.com updates
Management, pig farm management, work planning in each production stage: management in gestation, grow finish, batch farrowing
Compare production data, calculate the number of sow, nursery, and finishing spaces, and visualize your tasks on the work schedule by type of BMS.
Tool that allows you to calculate the replacement rate in your farm
Definition for the most commonly used pig terms
Weekly newsletter with all the pig333.com updates
Design of facilities and equipment for pig farms: building design, climate control, feeding systems, etc.
Biocheck.UGent is an independent, risk-based, scientific scoring system for assessing the quality of your on-farm biosecurity.
Environmental Footprint Calculator along the pork value chain.
Definition for the most commonly used pig terms
Simulator that calculates the amount of drug to add to the water when using a flow dispenser.
Use this tool to explore which slurry management strategy best fits your situation. Click on the flow chart or on the buttons within the text to navigate through the different parts of the tool.
Weekly newsletter with all the pig333.com updates
What makes us stand out is the quality and independence of our contents. Find out about the authors who make it possible. Our goal is to generate a virtual community of advanced users in the sector.

Dr. Montserrat Torremorell is currently the A.D Leman Chair in Swine Health and Productivity and an associate professor in the Department of Veterinary Population Medicine at the College of Veterinary Medicine. She earned her DVM degree from the University Autonomous of Barcelona in 1994 and her PhD from the University of Minnesota in 1999.
Dr. Torremorell joined the University of Minnesota in her current role in May 2009. Prior to that, she was employed at Genus/PIC, the largest swine breeding company in the world, in a range of roles related to health assurance and health research. Dr. Torremorell led the efforts in PRRSV elimination where PIC USA was able to move from 12% to 100% PRRSV negative status in 5 years. Dr. Torremorell also participated in the National PRRSV Elimination program in Chile and more recently has worked in swine influenza control and elimination. Dr. Torremorell has an extensive background in swine health, research, and production systems, including health improvement strategies, disease eradication, diagnostics and biosecurity programs, and health genomics.
Dr. Torremorell currently teaches a veterinary elective class in Veterinary Medicine and collaborates in other teaching activities related to swine diseases. She is also the director of the Swine Disease Eradication Center at the College of Veterinary Medicine at the University of Minnesota. Dr. Torremorell is the author of more than 40 peer-reviewed journal articles and more than 100 abstracts and articles in conference proceedings. Dr. Torremorell was awarded with the Allen D. Leman Science In Practice Award from Pfizer and the University of Minnesota in 2003 for the work on PRRS elimination. Her research interests include infectious diseases of swine focusing on influenza and other swine diseases of economic significance. For her influenza research, she is interested in further understanding SIV transmission, including aerosol transmission and factors that contribute to the persistence and spread of flu in populations. In addition she is interested in further elucidating strategies to control, eliminate and prevent flu infection in pigs and further understanding the interface pigs and people.
Updated CV 06-Oct-2013

Breaking the chain of infection from humans to pigs and from pigs to humans.

PRRS creates frustrating challenges as it seems we have to keep learning the same lessons we already know, along with the occasional new chapter.

Consider these factors when deciding to eliminate or control PRRSv.
Lessons learnt from two of the most important virologists of the north American swine industry, Dra. Torremorell and Dra. Culhane, from other coronavirus outbreaks than spread globally within the swine industry.
Nurse sows may represent a source of infection to the newly adopted pigs.
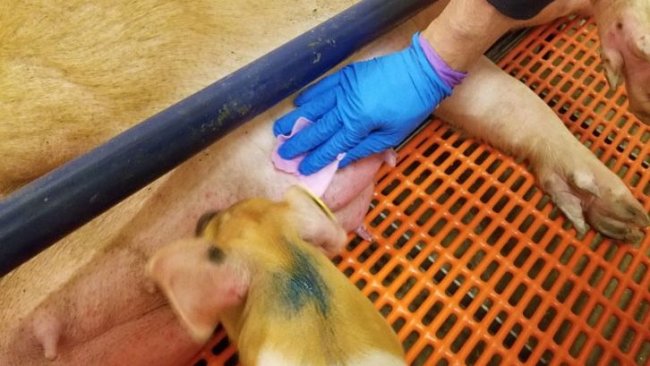
Montse Torremorell speaks about different alternatives that are being explored to obtain live animal samples at a reasonable cost.

We propose to use the processing fluids, the liquid accumulated at the bottom of the pail when farmers collect tails and testicles during routine procedures as a sample.
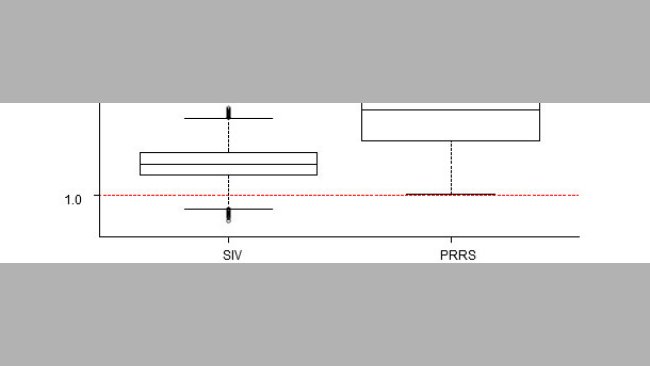
Infection with swine influenza virus and porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome during the suckling period was associated with an increase in post-weaning mortality (more limited in the case of SIV and of larger magnitude for PRRSV).

The most direct strategy to decrease the concentration in the air of airborne pathogens is dust reduction. This article describes the use of a particle ionization system called EPI.
Influenza infections are self-limiting at the individual animal level with infection lasting between 5 and 7 days approximately. However, influenza virus is considered endemic in swine populations worldwide, and is not uncommon to find between 3 and 5% of pigs positive to influenza virus at slaughter.
Replacement gilts recently introduced and piglets prior to weaning are the main risk groups.

One of the challenges when conducting a disease elimination project is to ensure that the pathogen has in deed been eliminated from the herd.
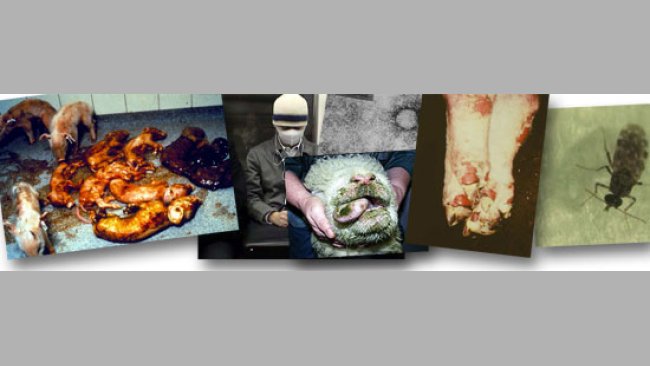
As better information systems capable to measure change in disease patterns, vector distribution and environmental conditions are put in place, we may be surprised about the range of diseases directly or indirectly already affected by climate change.

Welcome to 333
Connect, share, and interact with the largest community of professionals in the swine industry.
Celebrating 196373Users on 333!
Sign upAlready a member?





