The report, part of the European Surveillance of Veterinary Antimicrobial Consumption (ESVAC) project, presents data from 31 countries from the European Economic Area and Switzerland which voluntarily provided information on sales or prescriptions of veterinary antibiotics for 2017.
The findings of the report confirm the downward trend seen over the last few years and show that EU guidance and national campaigns promoting prudent use of antibiotics in animals to fight antimicrobial resistance are having a positive effect.

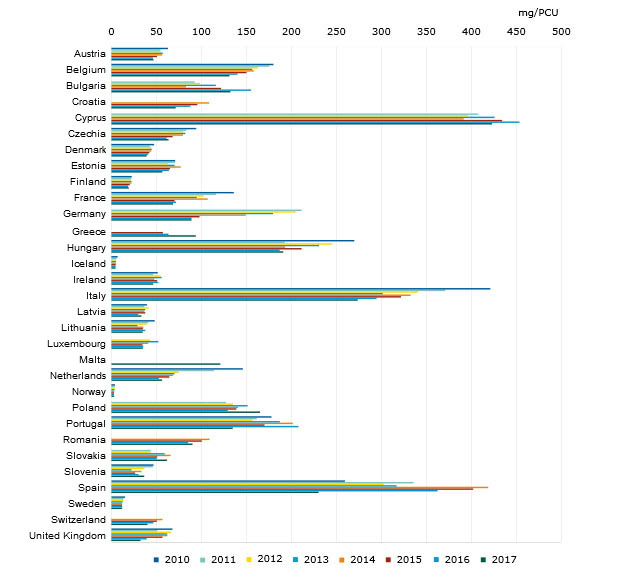
The ESVAC report shows that the situation is not the same across Europe. For the 25 countries that reported data for all years from 2011 to 2017, a drop of more than 5 % (range -7.7 % to -57.9 %) in sales (mg/PCU) was observed for 19 countries. For three countries, an increase of more than 5 % was noted (range 29.8 % to 42.9 %)
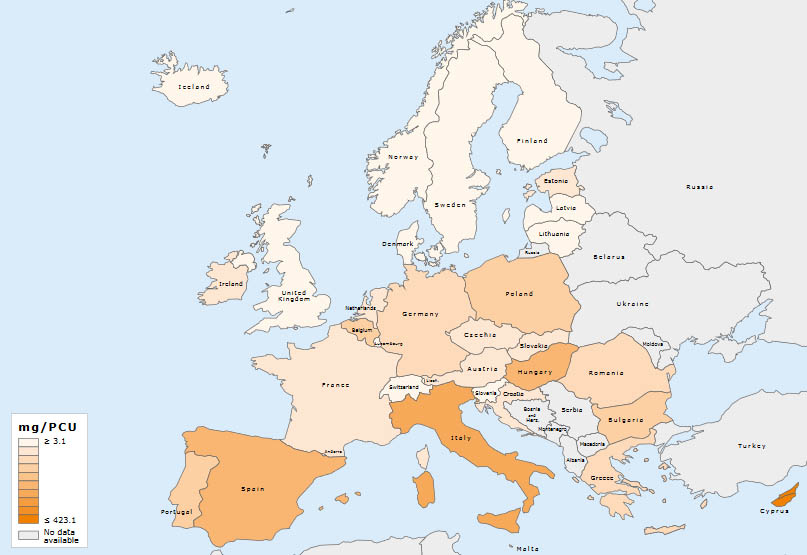
A large difference in the sales for 2017, expressed as mg/PCU, was observed between the countries with the highest and lowest sales (range 3.1 to 423.1 mg/PCU); total aggregated sales linked to aggregated PCU for all 31 countries which delivered data in 2017 was 107.0 mg/PCU, while the median was 61.9 mg/PCU.
Of the overall sales of antimicrobials in the 31 countries in 2017, the largest amounts, expressed as mg/PCU, were accounted for by tetracyclines (30.4 %), penicillins (26.9 %) and sulfonamides (9.2 %). Overall, these three classes accounted for 66.5 % of total sales in the 31 countries.
In particular, two of the critically important classes of antibiotics for human medicine were used less in animals: sales of polymyxins plummeted by 66% and sales of 3rd- and 4th-generation cephalosporins decreased by more than 20%. These classes include antibiotics used to treat serious infections in humans caused by bacteria resistant to most treatments.

Overall, pigs, cattle, poultry and sheep plus goats accounted for 32 %, 31 %, 14 % and 14 %, respectively, of the PCU in the 31 countries.
Wednesday October 16, 2019/ EMA/ European Union.
https://www.ema.europa.eu





