According to data from the 25 countries that provided input for the full 2011-2020 period, overall sales of veterinary antimicrobials in European countries were 43% lower in 2020 than in 2011.
While an increase of 6% in overall sales for the 25 countries in 2020 compared to 2019 was registered, data for the next years are necessary to better understand this observation.

Sales of those antimicrobials that are considered critically important in human medicine, decreased noticeably between 2011 and 2020 and accounted for only 6% of total sales in 2020. In particular, sales of third- and fourth- generation cephalosporins dropped by 33%, polymyxins by 76%, fluoroquinolones by 13% and sales of other quinolones dropped by 85%. These classes include antimicrobials used to treat serious infections in humans that are caused by bacteria resistant to most other antimicrobial treatments. In animals, they should be used with restrictions in order to preserve their effectiveness and mitigate the risk to public health, as indicated in the Antimicrobial Advice Ad Hoc Expert Group (AMEG) categorisation.
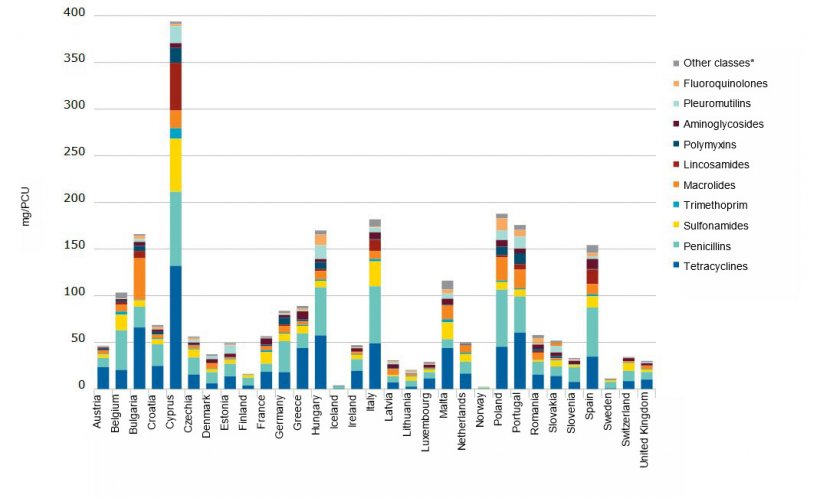
* ‘Other classes’ includes amphenicols, cephalosporins, other quinolones and ‘Others’.
1 Differences between countries can be partly explained by differences in animal demographics, occurrence of bacterial diseases, selection
of antimicrobial agents, dosage regimes, types of data source, and veterinarians’ prescribing habits.
November 23, 2021/ EMA.
https://www.ema.europa.eu/





