According to a report submitted to the OIE by Dr Toshiro Kawashima (Animal Health Division, Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries, Japan), in October 2013, an outbreak of PED was confirmed after an absence of 7 years. PED is a notifiable disease in Japan and there are PED vaccines approved by the Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries.
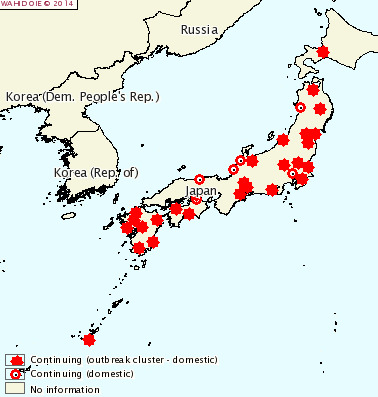
Number of outbreaks started to increase from December 2013 in the Southern Kyushu area. The number of outbreaks in the Southern Kyushu area temporarily decreased in February 2014, however, it started to increase again in March 2014 and at the same time, outbreaks were confirmed in the Northern Kyushu area and other prefectures in the Northern part of Japan. Numbers of newly affected prefectures by month are as follows: October (1), November (1), December (2), January (1), February (2), March (10), April (16).

According to the report, the total number of confirmed outbreaks to date is 418: Okinawa (4 ), Ibaraki (5), Kagoshima (156), Miyazaki (68), Kumamoto (20), Aichi (20), Aomori (10), Kochi (3), Okayama (2), Tottori (1), Saga (9), Oita (5), Fukuoka (4), Chiba (29), Nagasaki (6), Saitamamie (14), Kagawaehime (2), Tochigi (9), Gunma (6), Niigata (13), Shizuoka (5), Fukushima (2), Toyama (2), Ishikawa (1), Gifu (2), Yamagata (2), Hokkaido (3), Fukui (1), Iwate (8), Akita (1) and Miyagi (3).
According to genetic analysis by the National Institute of Animal Health, viruses isolated from the cases in October and November 2013 were close to the viruses isolated in the People’s Republic of China and the United States of America in 2013.
Friday April 25, 2014/ OIE.
http://www.oie.int



