Bronchopneumonia - Atlas of swine pathology

Where: respiratory system, lungs
Possible causes: Metastrongylosis
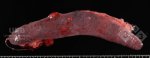
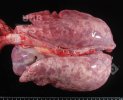
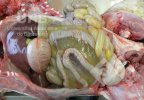
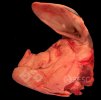
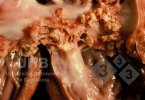
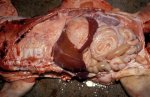
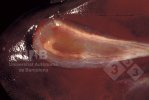
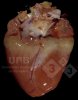
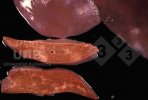
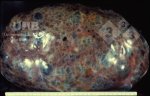
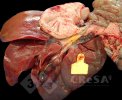
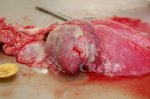
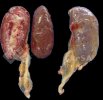
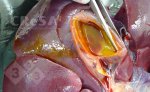
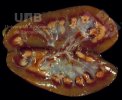
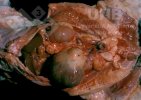
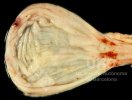
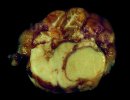
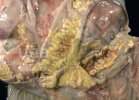
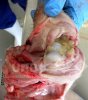
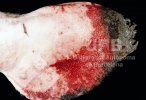
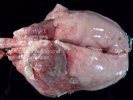
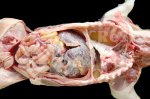
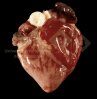
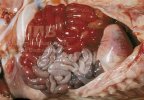
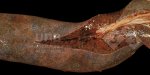
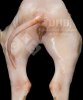
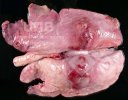
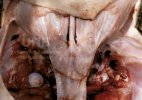
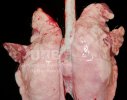
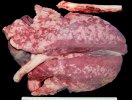
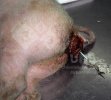
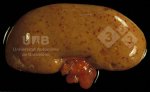
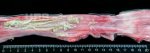
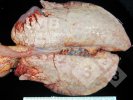
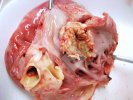
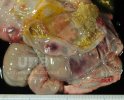
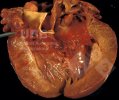
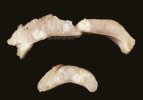
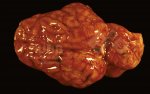
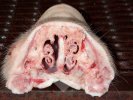
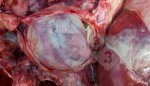
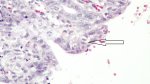
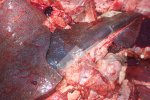
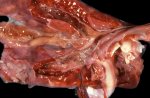
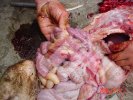
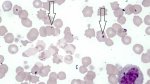
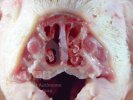
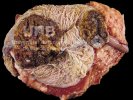
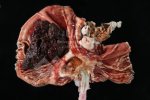
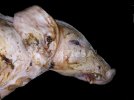
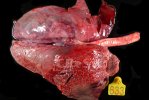
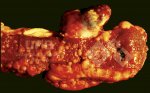
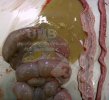
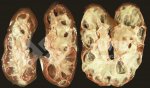
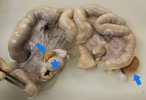
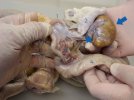
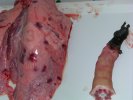
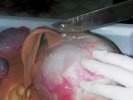
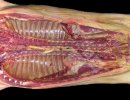
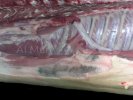
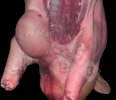
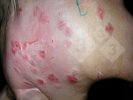
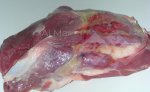
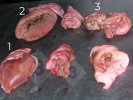
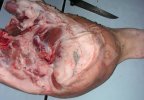
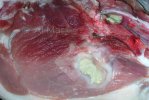
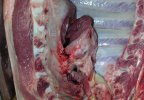
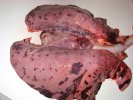
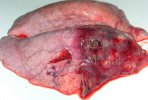
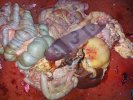
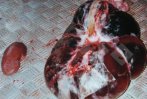
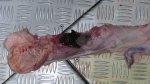
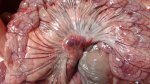
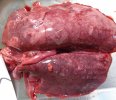
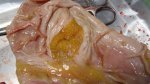
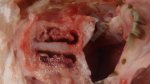
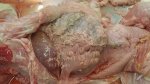
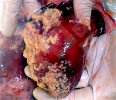
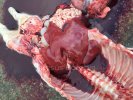
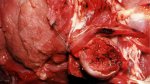
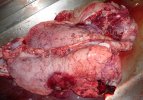
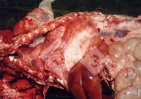
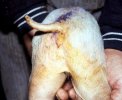
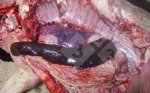
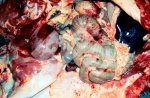
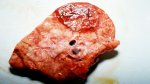
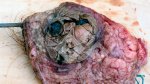
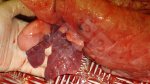
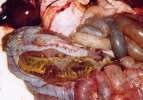
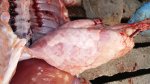
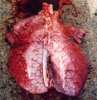
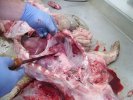
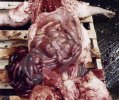
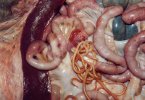
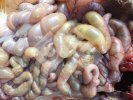
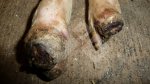
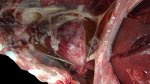
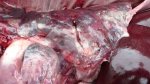
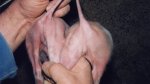
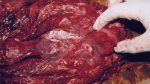
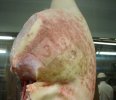
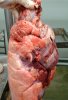
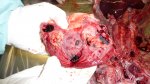
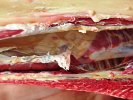
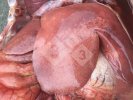
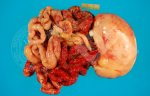
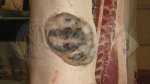
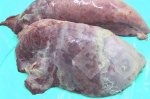
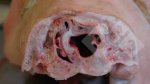
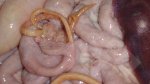
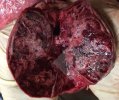
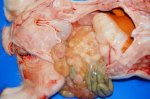
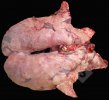
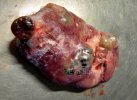
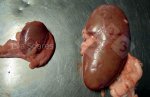
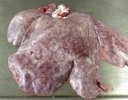
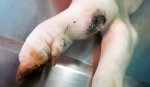
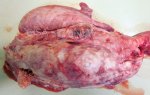
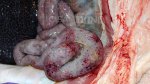
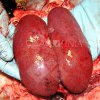
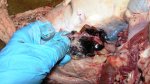
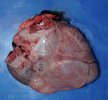
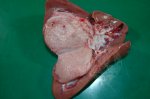
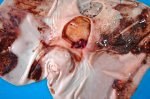
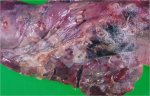
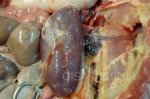
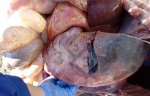
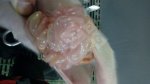
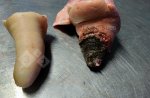
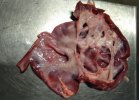
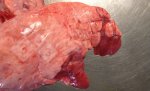
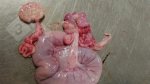
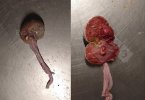
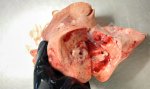
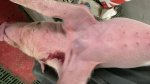
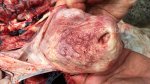
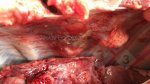
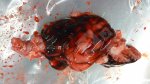
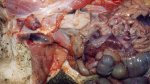
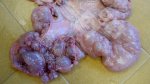
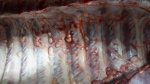
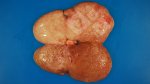
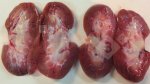
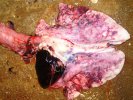
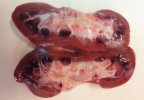
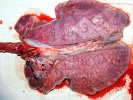
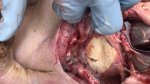
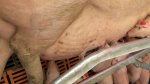
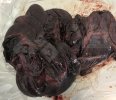
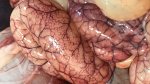
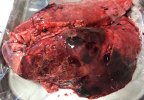
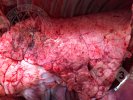
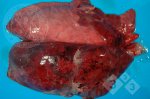
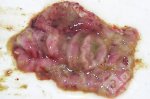
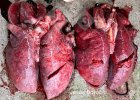
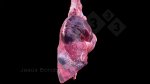
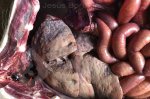
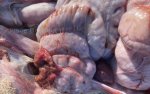
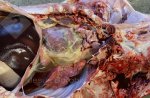
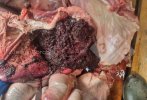
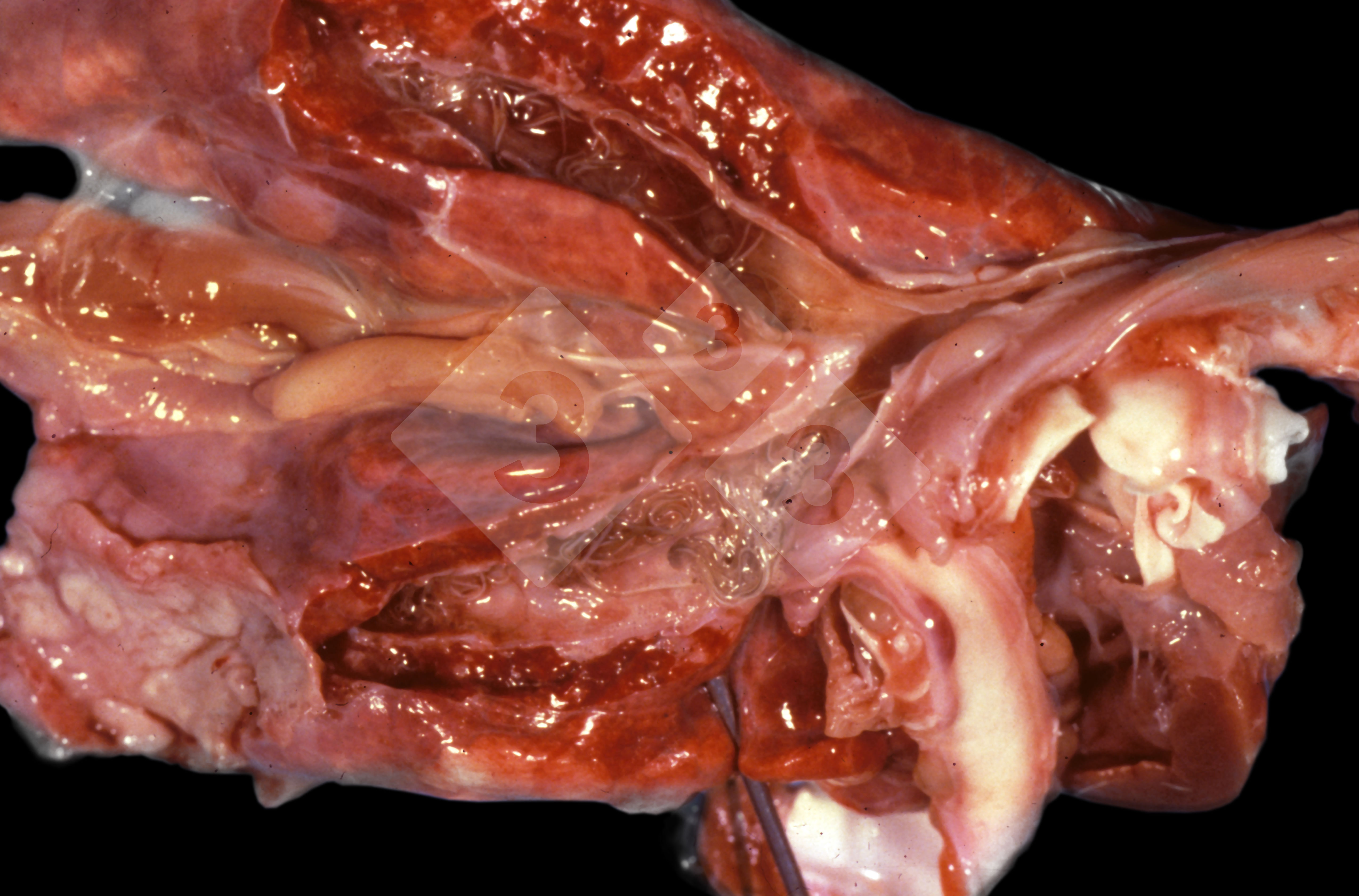
This is parasitic bronchopneumonia due to the specific lungworm of the pig, named Metastrongylus apri. These worms live in the bronchi and bronchioles of the pig lungs. Affected pigs may have poor body condition, with a deep chronic cough and difficulty breathing. At autopsy, the lungs and bronchial airway tree contain numerous 2 to 6 cm long thread-like worms inside the airways. The lung lobes may have moderate pneumonia, with dark purple consolidation, noticed at the outer edges of lobes. These adult M apri worms and their eggs and larvae produce an inflammation and irritant effect in the airways of the lungs, leading to a persistent cough. The life cycle of this worm is indirect, wherein the completion of the life cycle requires the intervention of earthworms on the ground. The life cycle is completed by pigs eating an earthworm that contains infective larvae inside it. Infection therefore only occurs where pigs have access to earthworms, for example in outdoor farms with open ground or orchards. This disease is still common in some areas where pigs kept outdoors. This is because the earthworm populations will retain the worms for long periods and pigs moving around on outdoor pastures are attracted by earthworms and will dig around trying to find them and eat them.