Lameness - Atlas of swine pathology

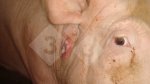
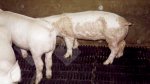
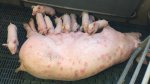
Where: musculoskeletal system
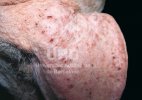
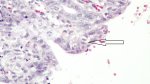
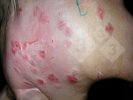
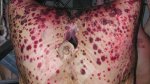
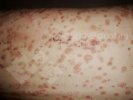
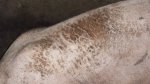
Possible causes: Biotin deficiency
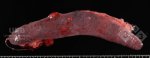
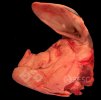
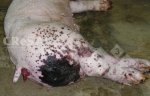
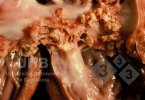
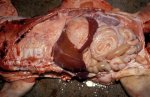
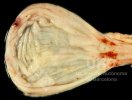
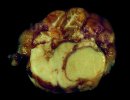
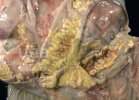
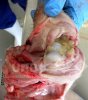
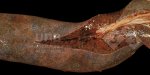
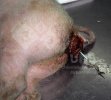
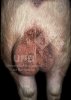
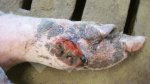
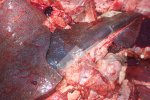
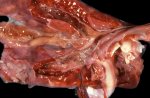
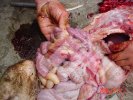
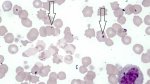
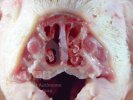
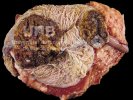
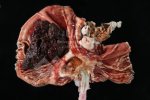
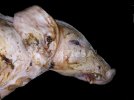
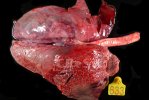
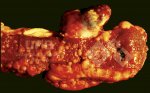
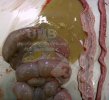
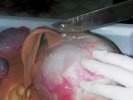
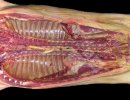
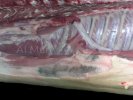
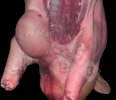
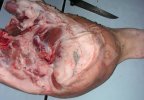
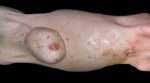
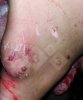
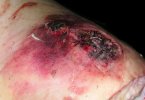
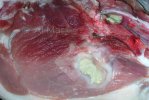
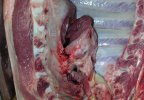
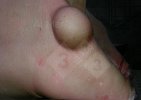
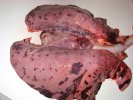
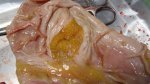
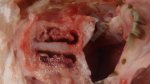
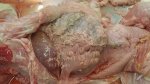
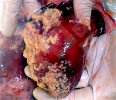
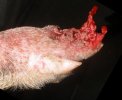
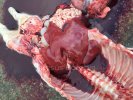
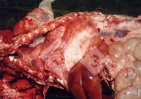
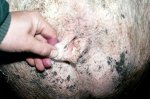
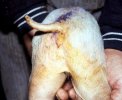
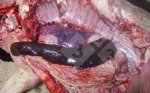
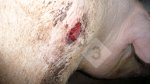
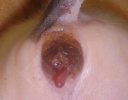
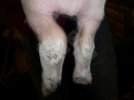
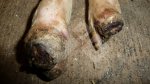
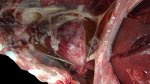
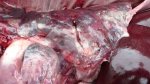
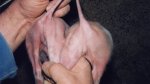
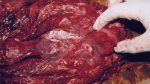
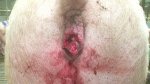
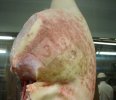
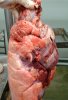
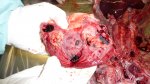
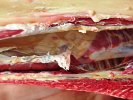
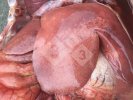
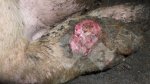
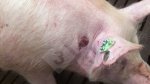
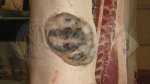
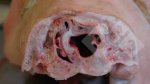
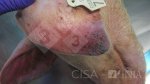
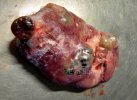
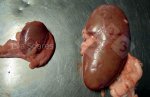
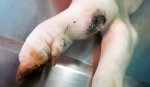
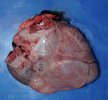
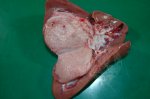
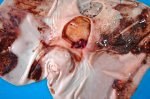
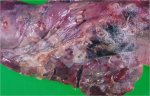
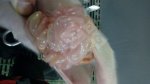
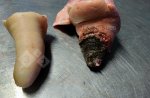
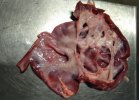
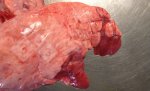
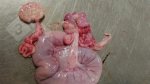
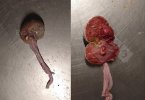
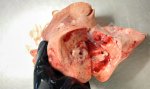
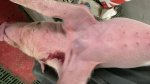
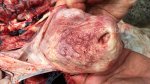
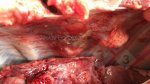
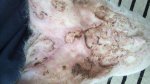
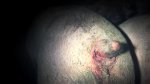
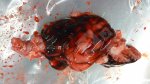
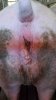
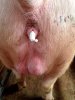
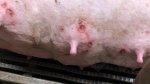
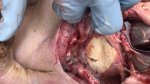
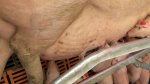
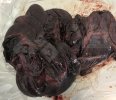
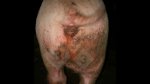
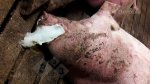
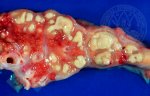
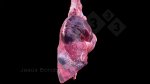
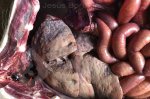
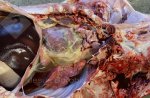
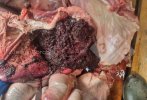
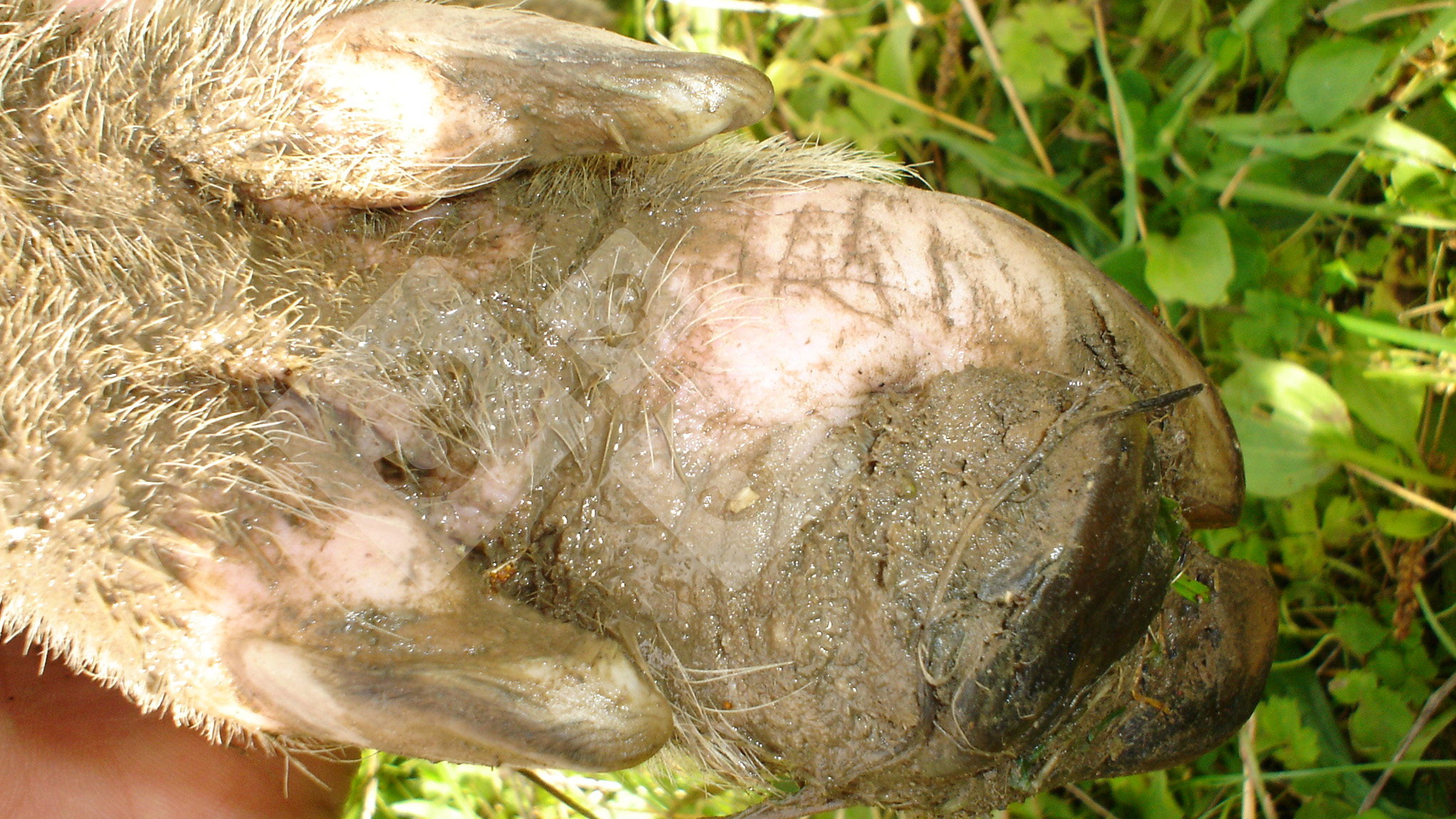
Foot rot involves both superficial and deep infection of the soft tissues between the claws often caused by fusiform bacteria. The claw becomes enlarged and inflamed. Invariably, unless foot rot has developed, only one claw is involved. All begin with some form of defect or penetration of the wall of the claw which provides a point of entry for secondary bacterial invasion such as Fusobacterium necrophorum, Arcanobacterium pyogenes and spirochaetes.
Treatment consists in cleaning the lesion and spray with an antibiotic. The animal may be given a course of antimicrobial.
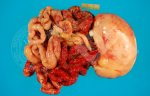
Affected animals which are able to be transported should be culled at the earliest opportunity if fit for slaughter, otherwise killed humanely.