Laboratory diagnostics: E. coli (diarrhea)
What laboratory diagnostic methods can I use to diagnose E. coli? Which one should I choose according to the situation? How do I interpret the results?
The pig sector events all around the world
Weekly newsletter with all the pig333.com updates
Swine industry news in your email
Pig health: news and articles on PRRS, PCV2, biosecurity, etc, Pig disease guide, atlas of pathology, clinical cases…
Biocheck.UGent is an independent, risk-based, scientific scoring system for assessing the quality of your on-farm biosecurity.
A visual and practical step-by-step guide on how to perform a necropsy on a pig.
All the information about ASF: how to recognize the disease, how it is transmitted, pictures of lesions, latest news, guides, etc.
All the information on Foot and Mouth Disease in pigs: how to recognize the disease, how it is transmitted, images of lesions, latest news, guides,...
Description of the most important diseases and conditions in pigs
Images of major swine diseases
Pig disease diagnostic tool
Definition for the most commonly used pig terms
Simulator that calculates the amount of drug to add to the water when using a flow dispenser.
Weekly newsletter with all the pig333.com updates
Pig Prices by countries. Pork production and trade. News of the pig market and the raw materials
The latest slaughter pig prices in the most important pig markets. Check the evolution of the historical prices in charts and in several currencies.
Latest quotations for the main commodities used in pig feed. Historical graphs with the pig price and estimated feed price.
Figures & trends in pig numbers, pork production and pork trade.
Global production and trade data for the most important raw materials
Weekly newsletter with all the pig333.com updates
Articles on nutrition and pig feeding, characteristics of raw materials and additives for pig feed. Prices of raw materials
Latest quotations for the main commodities used in pig feed. Historical graphs with the pig price and estimated feed price.
Technical sheets of the main raw materials and additives used in swine feed. They include a comparison of nutritional values from various sources, product
Global production and trade data for the most important raw materials
Definition for the most commonly used pig terms
Use this tool to diagnose problems with the feed conversion ratio. Click on the flowchart or on the buttons within the text to navigate through the different parts of the tool.
A biweekly newsletter with the latest developments in swine nutrition
Articles on genetics and pig reproduction: genetic improvement, genomics, artificial insemination, use of hormones
Compare production data, calculate the number of sow, nursery, and finishing spaces, and visualize your tasks on the work schedule by type of BMS.
Tool that allows you to calculate the replacement rate in your farm
Definition for the most commonly used pig terms
Use this tool to find out why your farrowing rate is less than ideal. Click on the flowchart or on the buttons found within the text to navigate through the different parts of the tool.
Weekly newsletter with all the pig333.com updates
Management, pig farm management, work planning in each production stage: management in gestation, grow finish, batch farrowing
Compare production data, calculate the number of sow, nursery, and finishing spaces, and visualize your tasks on the work schedule by type of BMS.
Tool that allows you to calculate the replacement rate in your farm
Definition for the most commonly used pig terms
Weekly newsletter with all the pig333.com updates
Design of facilities and equipment for pig farms: building design, climate control, feeding systems, etc.
Biocheck.UGent is an independent, risk-based, scientific scoring system for assessing the quality of your on-farm biosecurity.
Environmental Footprint Calculator along the pork value chain.
Definition for the most commonly used pig terms
Simulator that calculates the amount of drug to add to the water when using a flow dispenser.
Use this tool to explore which slurry management strategy best fits your situation. Click on the flow chart or on the buttons within the text to navigate through the different parts of the tool.
Weekly newsletter with all the pig333.com updates
List of the most important diseases and conditions in pigs. Symptoms, causes, diagnosis, control and prevention of each disease are described. Some of the treatments mentioned may be prohibited in some countries. Information on all diseases to be completed in the coming days.
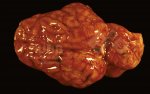
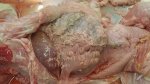
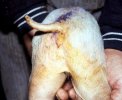
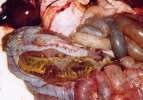
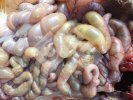
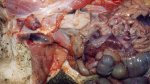
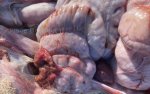
Diarrhea by E. coli affects mainly lactating piglets, causing high mortality.
Of all the diseases in piglets, diarrhea is the most common, and the most important. In some outbreaks mortality and morbidity are high. In well managed farms, less than 3% of the litters should need treatment at a given point in time and the mortality should be lower than 0.5%. In very severe outbreaks, mortality can be higher if litters are not treated.
The main causes of diarrhea in piglets are: E. coli, clostridium, coccidia, TGE virus, porcine epidemic diarrhea virus, rotavirus, and agalactia. E. coli is the most common.
When piglets are born, the gastrointestinal tract is microbiologically sterile and has low immunity to fight organisms causing disease. These organisms rapidly colonize the digestive tract after birth; amongst these organisms, strains of E. coli and Clostridium are potentially pathogenic. Immunity is initially obtained through colostrum, which contains high antibody levels (IgG and IgA). After being absorbed, colostrum antibodies enters the blood stream and the immunity is maintained through antibodies (IgA) present in milk (lactogenic protection). It is of paramount importance for newborn piglets to drink colostrum immediately after birth to avoid pathogenic organisms multiplying in the intestinal wall, causing diarrhea. It is also very important for the piglet to drink milk continuously, in order to keep the intestine covered with protecting antibodies (IgA).
Antibodies acquired in a passive way from colostrum and milk do not last forever and can be exceeded by the bacterial loads present in the environment. As the number of organisms ingested increases, the risk of disease increases. Environmental stress such as cold also has an important role because it decreases the piglets resistance. There is a delicate equilibrium between the level of antibodies and the infectious load together with stress.
In piglets younger than 5 days of age, the most common cause of acute diarrhea is E. coli, mainly in first parity sows. Clostridium infections are also produced at this age.
At weaning, the loss of milk intake and IgA, the expression of new intestinal receptors, and intestinal irritation due to change in diet (liquid milk based to dry plant protein) allows E. coli to adhere to the small intestine villi, and its toxins cause acute diarrhea, 5 to 14 days after weaning.
Sows and growers
Lactating piglets
Weaners
Sows and lactating piglets
Lactating piglets
Weaners

What laboratory diagnostic methods can I use to diagnose E. coli? Which one should I choose according to the situation? How do I interpret the results?