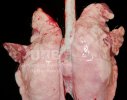
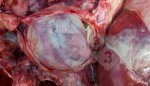
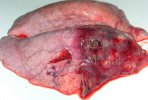
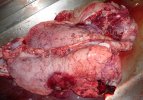
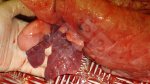
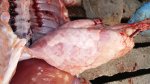
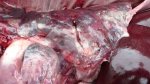
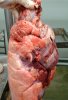
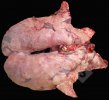
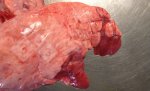
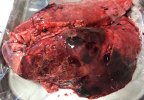
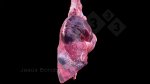
Impact of porcine enzootic pneumonia and pleuropneumonia on carcass weight and lean meat content
One percentage of affected lung volume was associated with a 0.24% reduction in lean meat content.
The pig sector events all around the world
Weekly newsletter with all the pig333.com updates
Swine industry news in your email
Pig health: news and articles on PRRS, PCV2, biosecurity, etc, Pig disease guide, atlas of pathology, clinical cases…
Biocheck.UGent is an independent, risk-based, scientific scoring system for assessing the quality of your on-farm biosecurity.
A visual and practical step-by-step guide on how to perform a necropsy on a pig.
All the information about ASF: how to recognize the disease, how it is transmitted, pictures of lesions, latest news, guides, etc.
All the information on Foot and Mouth Disease in pigs: how to recognize the disease, how it is transmitted, images of lesions, latest news, guides,...
Description of the most important diseases and conditions in pigs
Images of major swine diseases
Pig disease diagnostic tool
Definition for the most commonly used pig terms
Simulator that calculates the amount of drug to add to the water when using a flow dispenser.
Weekly newsletter with all the pig333.com updates
Pig Prices by countries. Pork production and trade. News of the pig market and the raw materials
The latest slaughter pig prices in the most important pig markets. Check the evolution of the historical prices in charts and in several currencies.
Latest quotations for the main commodities used in pig feed. Historical graphs with the pig price and estimated feed price.
Figures & trends in pig numbers, pork production and pork trade.
Global production and trade data for the most important raw materials
Weekly newsletter with all the pig333.com updates
Articles on nutrition and pig feeding, characteristics of raw materials and additives for pig feed. Prices of raw materials
Latest quotations for the main commodities used in pig feed. Historical graphs with the pig price and estimated feed price.
Technical sheets of the main raw materials and additives used in swine feed. They include a comparison of nutritional values from various sources, product
Global production and trade data for the most important raw materials
Definition for the most commonly used pig terms
Use this tool to diagnose problems with the feed conversion ratio. Click on the flowchart or on the buttons within the text to navigate through the different parts of the tool.
A biweekly newsletter with the latest developments in swine nutrition
Articles on genetics and pig reproduction: genetic improvement, genomics, artificial insemination, use of hormones
Compare production data, calculate the number of sow, nursery, and finishing spaces, and visualize your tasks on the work schedule by type of BMS.
Tool that allows you to calculate the replacement rate in your farm
Definition for the most commonly used pig terms
Use this tool to find out why your farrowing rate is less than ideal. Click on the flowchart or on the buttons found within the text to navigate through the different parts of the tool.
Weekly newsletter with all the pig333.com updates
Management, pig farm management, work planning in each production stage: management in gestation, grow finish, batch farrowing
Compare production data, calculate the number of sow, nursery, and finishing spaces, and visualize your tasks on the work schedule by type of BMS.
Tool that allows you to calculate the replacement rate in your farm
Definition for the most commonly used pig terms
Weekly newsletter with all the pig333.com updates
Design of facilities and equipment for pig farms: building design, climate control, feeding systems, etc.
Biocheck.UGent is an independent, risk-based, scientific scoring system for assessing the quality of your on-farm biosecurity.
Environmental Footprint Calculator along the pork value chain.
Definition for the most commonly used pig terms
Simulator that calculates the amount of drug to add to the water when using a flow dispenser.
Use this tool to explore which slurry management strategy best fits your situation. Click on the flow chart or on the buttons within the text to navigate through the different parts of the tool.
Weekly newsletter with all the pig333.com updates
List of the most important diseases and conditions in pigs. Symptoms, causes, diagnosis, control and prevention of each disease are described. Some of the treatments mentioned may be prohibited in some countries. Information on all diseases to be completed in the coming days.
The main issue associated with M. hyopneumoniae infections is chronic respiratory disease. This pathogen usually amplifies the severity of other infections, including flu and PRRS.
It is a chronic swine disease of big importance globally. Its chronic presentation is frequent in production farms working under continuous flow. The organism grows slowly, thus the disease manifests at 7 or 12 weeks of age, and is part of the porcine respiratory disease complex. It is treated with antibiotics and prevented with vaccination.
Enzootic pneumonia is caused by Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae, a bacteria that does not have cellular wall. It is widely spread in swine populations and is endemic in most of the farms globally. It always attacks the ciliated epithelium in the inferior parts of each lung lobe, producing tissue consolidation (typical of a pulmonary bacterial infection).
The main problem associated to M. hyopneumoniae infections is chronic respiratory disease, which can be associated to a dry and nonproductive cough. The disease has high morbidity and a low mortality, and it has a strong effect on average daily gain and feed conversion ratio.
If enzootic pneumonia is not present in the grower population, the effect of the other pathogens decreases significantly. Thus, it is considered a pathogen that increases the severity of other infections, including influenza and PRRS.
Disease occurs when enzootic pneumonia appears for the first time in a farm. For a period of 2 to 4 weeks after the bacteria enters the farm, an acute intense pneumonia with high mortality in pigs of all ages is observed.
The transmission is mainly through direct contact (nose to nose). The risk of transmission decreases in the farrowing area, with the age of the sows.
Affects all ages but is not clinically frequent in animals 6 weeks or younger. Its incubation period is 2 to 8 weeks.
Clinical symptoms include:
The increase of the clinical disease is associated to the following factors:
Based on clinical signs and post-mortem examinations, sometimes combined with histology of the lesions. However, these tools do not bring a specific diagnosis, and in farms producing reproductive animals or in special cases, it might be necessary to confirm the diagnosis through one or more of the following tests: ELISA, serological tests, microscopical examination of lung stained touch preparations, immunofluorescence tests, PCR and culture and identification of Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae.
These analyses are not available in all laboratories. PCR is the most sensitive method.
Enzootic pneumonia must be differentiated from influenza, PRRS, Glässer disease and other bacterial infections. Laboratory analyses are needed to differentiate them. In addition, all or some of these infections can be present together with Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae.
Diet medication might be necessary if:
In acute outbreaks or endemic herds consider the following factors:
Inactivated vaccines against Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae are very effective if they are administered early (before 5 weeks of age) and when the animals are not exposed to the replication of the PRRS virus.

One percentage of affected lung volume was associated with a 0.24% reduction in lean meat content.

This article presents the main characteristics of the vaccines that can be found on the market.

What laboratory diagnostic methods can I use to diagnose M. hyo? Which one should I choose according to the situation? How do I interpret the results?