Laboratory diagnostics: Streptococcus suis infection
What laboratory diagnostic methods can I use to diagnose Streptococcus suis? Which one should I choose according to the situation? How do I interpret the results?
The pig sector events all around the world
Weekly newsletter with all the pig333.com updates
Swine industry news in your email
Pig health: news and articles on PRRS, PCV2, biosecurity, etc, Pig disease guide, atlas of pathology, clinical cases…
Biocheck.UGent is an independent, risk-based, scientific scoring system for assessing the quality of your on-farm biosecurity.
A visual and practical step-by-step guide on how to perform a necropsy on a pig.
All the information about ASF: how to recognize the disease, how it is transmitted, pictures of lesions, latest news, guides, etc.
Description of the most important diseases and conditions in pigs
Images of major swine diseases
Pig disease diagnostic tool
Definition for the most commonly used pig terms
Simulator that calculates the amount of drug to add to the water when using a flow dispenser.
Weekly newsletter with all the pig333.com updates
Pig Prices by countries. Pork production and trade. News of the pig market and the raw materials
The latest slaughter pig prices in the most important pig markets. Check the evolution of the historical prices in charts and in several currencies.
Latest quotations for the main commodities used in pig feed. Historical graphs with the pig price and estimated feed price.
Figures & trends in pig numbers, pork production and pork trade.
Global production and trade data for the most important raw materials
Weekly newsletter with all the pig333.com updates
Articles on nutrition and pig feeding, characteristics of raw materials and additives for pig feed. Prices of raw materials
Latest quotations for the main commodities used in pig feed. Historical graphs with the pig price and estimated feed price.
Technical sheets of the main raw materials and additives used in swine feed. They include a comparison of nutritional values from various sources, product
Global production and trade data for the most important raw materials
Definition for the most commonly used pig terms
Use this tool to diagnose problems with the feed conversion ratio. Click on the flowchart or on the buttons within the text to navigate through the different parts of the tool.
A biweekly newsletter with the latest developments in swine nutrition
Articles on genetics and pig reproduction: genetic improvement, genomics, artificial insemination, use of hormones
Compare production data, calculate the number of sow, nursery, and finishing spaces, and visualize your tasks on the work schedule by type of BMS.
Tool that allows you to calculate the replacement rate in your farm
Definition for the most commonly used pig terms
Use this tool to find out why your farrowing rate is less than ideal. Click on the flowchart or on the buttons found within the text to navigate through the different parts of the tool.
Weekly newsletter with all the pig333.com updates
Management, pig farm management, work planning in each production stage: management in gestation, grow finish, batch farrowing
Compare production data, calculate the number of sow, nursery, and finishing spaces, and visualize your tasks on the work schedule by type of BMS.
Tool that allows you to calculate the replacement rate in your farm
Definition for the most commonly used pig terms
Weekly newsletter with all the pig333.com updates
Design of facilities and equipment for pig farms: building design, climate control, feeding systems, etc.
Biocheck.UGent is an independent, risk-based, scientific scoring system for assessing the quality of your on-farm biosecurity.
Environmental Footprint Calculator along the pork value chain.
Definition for the most commonly used pig terms
Simulator that calculates the amount of drug to add to the water when using a flow dispenser.
Use this tool to explore which slurry management strategy best fits your situation. Click on the flow chart or on the buttons within the text to navigate through the different parts of the tool.
Weekly newsletter with all the pig333.com updates
List of the most important diseases and conditions in pigs. Symptoms, causes, diagnosis, control and prevention of each disease are described. Some of the treatments mentioned may be prohibited in some countries. Information on all diseases to be completed in the coming days.
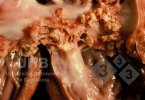
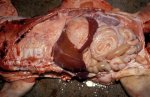
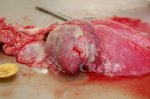
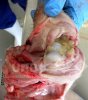
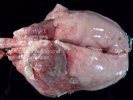
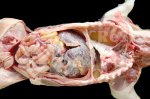
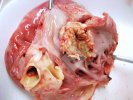
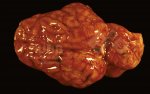
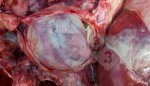
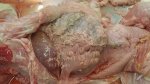
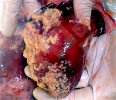
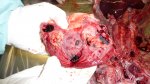
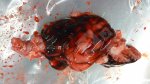
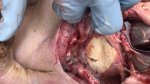
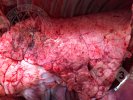
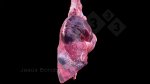
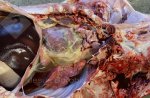
Streptococcus suis is the most important streptococcus of pigs causing pneumonia, septicemia, arthritis and encephalitis in pigs and is also of great public importance for its zoonotic potential.
Alternative names: Streptococcus suis, Streptococcus equisimilis, Streptococcus porcinus
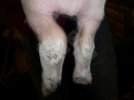
The streptococci are common organisms in all animals. Generally, but not always, they are specie specific. The main species present in pigs is Streptococcus suis which is widespread through all swine populations. It is associated with a variety of diseases including meningitis, septicemia, polyserositis, arthritis, endocarditis and pneumonia. It has also been isolated in cases of abortion and rhinitis. The pattern and the relative importance of different syndromes varies by country.
S. suis is subdivided into at least thirty five serotypes. They vary in pathogenicity and clinical signs they produce, between and within the different types. Some types appear to be non-pathogenic and have been isolated mainly from healthy animals, some are mainly associated with pulmonary lesions and some have been isolated from other animals besides swine. Some types, especially type 2, can cause meningitis in humans in addition to pigs. Fortunately human cases are rare.
For a farmer it is important and of concern the endemic meningitis caused by type 2. Clinically healthy animals may carry the organism in their tonsils for many months and there are sows that are carriers. There is still no technique available to eradicate a serotype once it has entered the farm and sets itself as part of the normal flora. S. suis is rapidly eliminated through disinfectants used in farms, including phenolic disinfectants, with chlorine and iodophors. Detergents also eliminate the organism in thirty minutes.
The sow passes antibodies through the colostrum to nursing piglets and therefore the disease is rare in this group unless it is entering into the farm for the first time. It is much more common to see it starting 2 or 3 weeks after weaning and it continues until 16 weeks of age. In farrowing almost 100% of pigs become carriers in three weeks.
PRRS can also increase the incidence of meningitis caused by pathogenic strains when it first enters in the farm.
Other Streptococcus species other than S. suis can cause diseases in pigs. For example, Streptococcus equisimilis produces sporadic cases of septicemia and arthritis in lactating piglets, heart valve infections in growing pigs and ascending infection of the uterus in sows. In the USA Streptococcus porcinus causes abscesses in the throat and septicemia, and sometimes is isolate from cases of pneumonia. However, cases of throat abscesses due to streptococcus have become rare in modern swine production facilities.
Sows
Lactating piglets, nursery and fattening

What laboratory diagnostic methods can I use to diagnose Streptococcus suis? Which one should I choose according to the situation? How do I interpret the results?

S. suis outbreaks are frequently associated with co-infections and stress factors identified as potential triggers, but the natural infection process is not fully understood, so, we wanted to know what the condition is for naturally affected pigs.